Understanding Hydro static Water Pressure and Its Impact on Solenoid Valves
What Is Hydro-static Water Pressure?
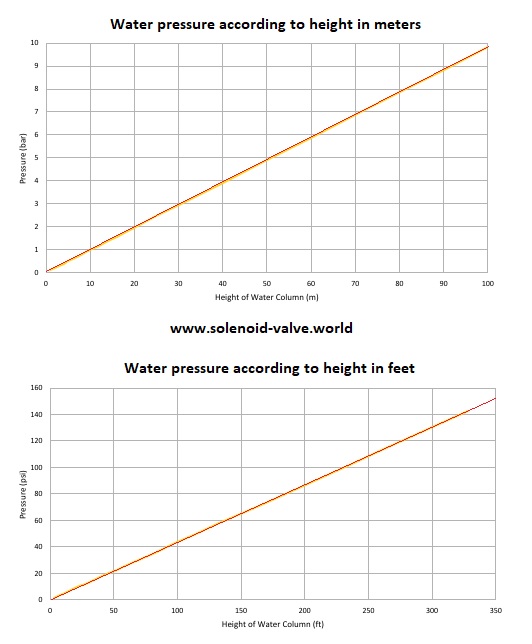
Hydro-static water pressure refers to the pressure exerted by a fluid at equilibrium due to the force of gravity. In water systems, this pressure increases proportionally with the height of the water column. For instance, a water column 10 meters high exerts approximately 1 bar of pressure.
Importance in Solenoid Valve Applications
Selecting the Right Solenoid Valve Based on Pressure
When designing or maintaining water systems, it's crucial to select solenoid valves that can handle the specific hydro-static pressures present. Using valves not rated for the system's pressure can lead to failures or inefficiencies.
Common Applications Affected by Hydro-static Pressure
Gravity-fed water systems: These rely on elevation to provide pressure, making accurate pressure calculations essential.
High-rise building plumbing: Taller structures experience higher pressures at lower levels.
Industrial processes: Systems involving tanks or reservoirs at varying heights must account for hydro-static pressure to ensure proper valve operation.
Calculating Hydrostatic Pressure
Basic Formula
Hydrostatic pressure can be calculated using the formula:
Pressure (P) = Height (h) × Density (ρ) × Gravitational acceleration (g)
h = height of the fluid column (in meters)
ρ = density of the fluid (for water, approximately 1000 kg/m³)
g = acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²)
Practical Examples
A 5-meter-high water column:
P = 5 × 1000 × 9.81 = 49,050 Pascals ≈ 0.49 bar
A 20-meter-high water column:
P = 20 × 1000 × 9.81 = 196,200 Pascals ≈ 1.96 bar
Choosing Solenoid Valves for Specific Pressure Ranges
Low to Medium Pressure (0–10 bar)
For applications within this range, consider:
WRAS approved brass solenoid valves: Suitable for potable water systems and compliant with UK water regulations.
High Pressure (10–150 bar)
Applications requiring higher pressure tolerance might utilise:
Brass solenoid valves rated up to 150 bar: Ideal for systems where higher pressures are encountered.
Very High Pressure (150–600 bar)
For extremely high-pressure systems:
Stainless steel solenoid valves rated up to 600 bar: Designed for durability and resistance in demanding environments.
Additional Considerations
Valve Functionality
Normally Closed (NC): Valve remains closed when de-energised; opens when power is applied.
Normally Open (NO): Valve remains open when de-energised; closes when power is applied.
Material Selection
Brass: Commonly used for water applications; offers good corrosion resistance.
Stainless Steel: Preferred for aggressive media or higher pressure requirements due to its superior strength and corrosion resistance.
Seal Materials
PTFE (Teflon): Suitable for a wide range of chemicals and temperatures.
NBR (Nitrile Rubber): Good for general-purpose applications involving water, oils, and some chemicals.
Conclusion
Understanding hydrostatic water pressure is essential for selecting the appropriate solenoid valves in any water system. By calculating the pressure based on the height of the water column and considering the specific requirements of your application, you can ensure efficient and safe operation.
For a comprehensive selection of solenoid valves tailored to various pressure requirements, contact us.
Water Column Height and Pressure Conversion Tables
| Height of Water Column |
Pressure |
||||
| (m) |
(ft) |
(kPa) |
(Bar) |
(atm) |
(psi) |
| 1 |
3.28 |
9.81 |
0.098 |
0.097 |
1.42 |
| 2 |
6.56 |
19.6 |
0.196 |
0.194 |
2.85 |
| 3 |
9.84 |
29.4 |
0.294 |
0.290 |
4.27 |
| 4 |
13.1 |
39.2 |
0.392 |
0.387 |
5.69 |
| 5 |
16.4 |
49.1 |
0.491 |
0.484 |
7.11 |
| 6 |
19.7 |
58.9 |
0.589 |
0.581 |
8.54 |
| 7 |
23.0 |
68.7 |
0.687 |
0.678 |
10.0 |
| 8 |
26.2 |
78.5 |
0.785 |
0.775 |
11.4 |
| 9 |
29.5 |
88.3 |
0.883 |
0.871 |
12.8 |
| 10 |
32.8 |
98.1 |
0.981 |
0.968 |
14.2 |
| 12 |
39.4 |
118 |
1.18 |
1.16 |
17.1 |
| 14 |
45.9 |
137 |
1.37 |
1.36 |
19.9 |
| 16 |
52.5 |
157 |
1.57 |
1.55 |
22.8 |
| 18 |
59.0 |
177 |
1.77 |
1.74 |
25.6 |
| 20 |
65.6 |
196 |
1.96 |
1.94 |
28.5 |
| 25 |
82.0 |
245 |
2.45 |
2.42 |
35.6 |
| 30 |
98.4 |
294 |
2.94 |
2.90 |
42.7 |
| 35 |
115 |
343 |
3.43 |
3.39 |
49.8 |
| 40 |
131 |
392 |
3.92 |
3.87 |
56.9 |
| 50 |
164 |
491 |
4.91 |
4.84 |
71.1 |
| 60 |
197 |
589 |
5.89 |
5.81 |
85.4 |
| 70 |
230 |
687 |
6.87 |
6.78 |
100 |
| 80 |
262 |
785 |
7.85 |
7.75 |
114 |
| 90 |
295 |
883 |
8.83 |
8.71 |
128 |
| 100 |
328 |
981 |
9.81 |
9.68 |
142 |
Useful link: Pressure unit conversion guide.
Find valves for Water, WRAS approved valves for water or valves for RO water

