NPT vs BSPT The Ultimate Pipe Thread Comparison Guide
Let's get one thing straight right from the start: NPT and BSPT threads are not interchangeable. You simply cannot connect them directly and expect a good result. Trying to do so is a guaranteed recipe for a failed seal, leaks, and potential system damage.
NPT (National Pipe Thread) is the go-to standard in America, while BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) is the dominant choice across the UK and Europe.
Understanding Why NPT and BSPT Are Not Interchangeable
Choosing the wrong thread type is one of the most common—and expensive—mistakes we see in plumbing, hydraulics, and pneumatics. At a quick glance, NPT and BSPT fittings look deceptively similar, but they come from entirely different engineering philosophies and geographical histories. Mixing them creates a weak point in your system that is almost certain to leak, especially once you add pressure.
This isn't some arbitrary difference; it's the result of over a century of separate industrial development. The National Pipe Thread (NPT) was standardised in the United States, designed with a 60-degree thread angle, and it has served North American markets ever since.
On the other hand, British Standard Pipe Taper (BSPT) threads grew out of British engineering practices and feature a 55-degree thread angle. This standard is so ingrained that today in the UK, over 95% of threaded pipe fittings in sectors from construction to utilities are either BSP or BSPT—a clear legacy of the British Empire's engineering influence. You can dig deeper into these historical standards in our full guide on worldwide thread information.
Geographical and Engineering Divergence
The fundamental reason you can't mix these threads boils down to their design specifications, which were developed independently to solve regional industrial challenges.
North American Standard (NPT): Standardised by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), NPT became the default choice for general industrial and plumbing work across the US and Canada. Its design is clever but simple: it relies on the threads deforming as they tighten to create a seal.
UK and European Standard (BSPT): Made official by the British Standards Institution (BSI), BSPT became the standard in the UK, Europe, and many Commonwealth nations. It is deeply embedded in UK infrastructure, as laid out in specifications like BS EN 10226-1:2004.
Crucial Takeaway: The problem isn't just about different measurements; it's a direct conflict in engineering. The mismatched thread angles (60° for NPT vs. 55° for BSPT) and different pitches prevent the threads from ever mating properly. They simply can't mesh together to form a secure, leak-proof seal. Understanding this is the first and most important step to building a safe and reliable system.
A Detailed Comparison of Thread Geometry and Design
To the untrained eye, NPT and BSPT threads can look deceptively similar. However, a closer inspection of their core geometry reveals precisely why they are fundamentally incompatible. These small, technical differences in their design DNA dictate everything from how they seal to where they are used across the globe.
The most critical difference is the thread flank angle. NPT threads, designed to American standards (ANSI), are machined with a 60-degree angle. In contrast, BSPT threads follow British standards and feature a slightly sharper 55-degree angle. This five-degree difference is the primary culprit behind failed connections; the threads simply cannot engage with each other properly, leading to a poor fit and inevitable leaks.
This image gives a great close-up view of the tapered design that defines NPT threads.
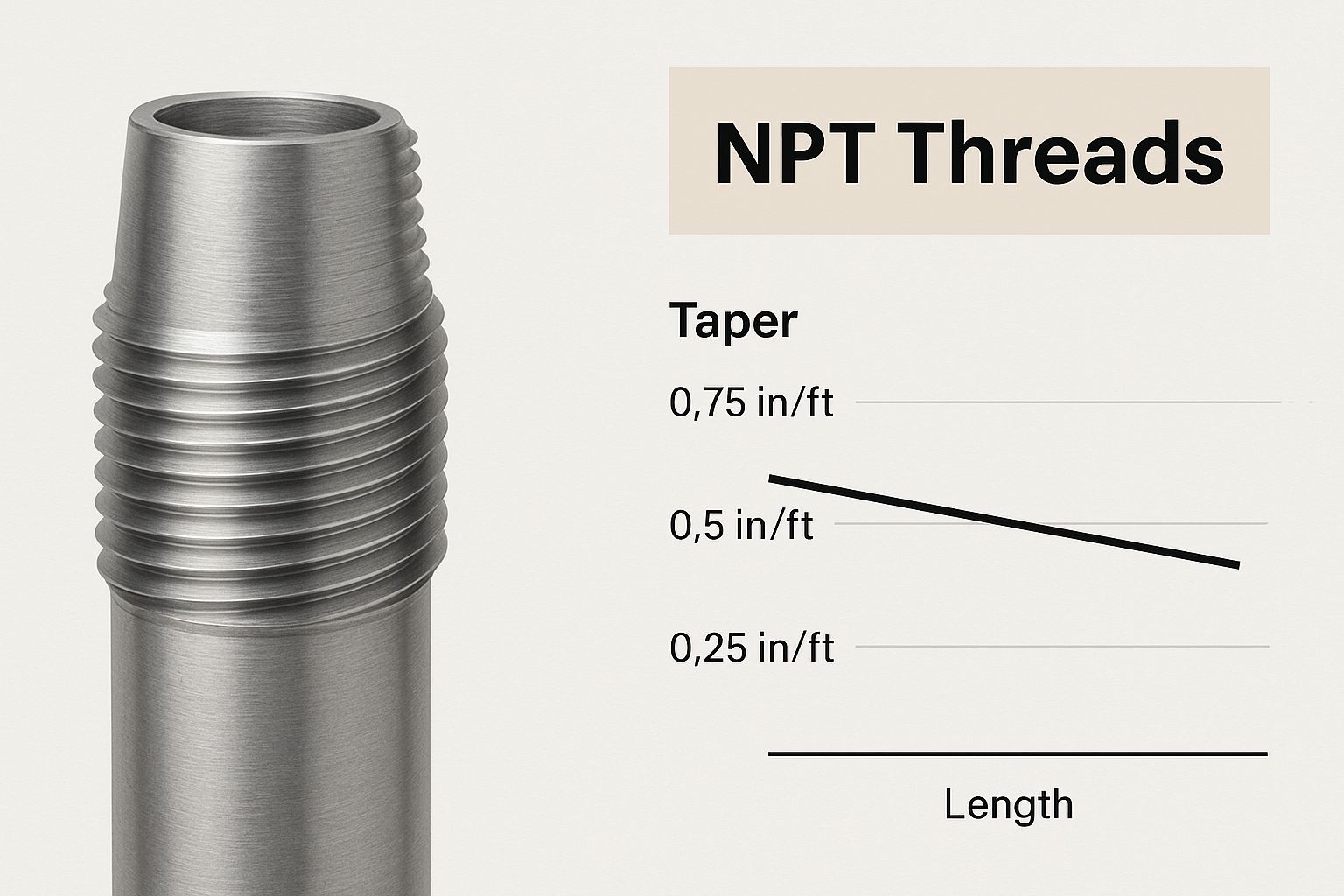
As you can see, the conical shape is what allows NPT fittings to create a tight seal through thread deformation—a key part of their design.
Thread Profile and Pitch: More Than Just Angles
Beyond the flank angle, the actual shape of the threads is another point of divergence. NPT threads have flattened crests and roots, which creates a more robust, utilitarian profile. BSPT threads, on the other hand, are engineered with rounded crests and roots. This rounded profile results in a different sealing dynamic, one that aims for more precise metal-to-metal contact along the thread flanks rather than relying on deformation alone.
Finally, we have to talk about thread pitch. While you might get lucky and find that some NPT and BSPT sizes have the same number of threads per inch (TPI), many do not. For example, a 1/2" NPT fitting has 14 TPI, and so does a 1/2" BSPT fitting. So far, so good. But step up to a 1" NPT fitting, and you get 11.5 TPI, whereas a 1" BSPT fitting has 11 TPI. These small yet critical differences in pitch make any attempt to mix and match them a recipe for disaster.
The bottom line: When you combine a different flank angle (60° vs 55°), a different thread profile (flattened vs rounded), and varying pitches, it becomes clear. NPT and BSPT threads can never form a secure, reliable seal when mated together.
NPT vs BSPT Technical Specifications
To lay it all out clearly, this table gives you a side-by-side comparison of the fundamental geometric differences. For any engineer or technician working with fluid power systems, especially when sourcing equipment from different parts of the world, knowing these details is non-negotiable.
| Attribute | NPT (National Pipe Thread) | BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Angle | 60 degrees | 55 degrees |
| Thread Profile | Flattened crests and roots | Rounded crests and roots |
| Taper Angle | 1° 47’ (1.7833 degrees) | 1° 47’ (1.7833 degrees) |
| Pitch Measurement | Threads Per Inch (TPI) | Threads Per Inch (TPI) |
| Regional Standard | Primarily North America (ANSI) | Primarily UK, Europe, Asia (BSI) |
The table makes it obvious: while both threads share the same taper, every other critical design element is different. These aren't accidental variations; they are intentional engineering choices that have resulted in two completely distinct and non-interchangeable systems for connecting pipes, valves, and fittings.
Comparing Sealing Methods and Performance

Those subtle differences in thread geometry between NPT and BSPT? They lead to completely different strategies for creating a leak-proof seal. Getting your head around these sealing mechanisms is crucial, especially in high-stakes industrial environments where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
NPT threads are designed to create what's known as an interference fit. As you tighten the male and female threads, their tapered design forces them to deform and literally crush together. This forceful mashing of metal is what creates the seal, but it's not a perfect solution. A tiny spiral leak path always remains along the thread crests. That's why using a quality thread sealant or PTFE tape is not optional, but mandatory for any NPT connection.
The Challenge of NPT Sealing
This reliance on thread deformation comes with a major risk: galling. This is what happens when the metal surfaces seize up during tightening, chewing up the threads and making disassembly—or getting a good seal in the future—a real headache. Over-tightening, a common mistake when chasing a leak, just makes it worse.
In contrast, BSPT threads use a much more precise and robust sealing method.
The core principle of a BSPT connection is a metal-to-metal seal that happens primarily on the flanks of the threads. The 55° angle allows for more precise contact between the male and female threads, creating a tight seal without needing significant deformation.
While sealant is still recommended for BSPT fittings, its job is different. It acts more as a lubricant to prevent galling and as a secondary backup against leaks, rather than being the primary sealing agent. This design makes BSPT inherently more reliable for high-pressure work, which is why you see it so often in hydraulic and pneumatic systems across the UK and Europe.
Performance Under Pressure
From a practical, real-world safety perspective, BSPT threads are favoured over NPT in the UK. They offer superior sealing efficiency and meet strict regulatory standards.
In head-to-head pressure tests, BSPT fittings have been shown to maintain their integrity without leaking at pressures up to 30% higher than their NPT counterparts. What's more, field data from UK infrastructure agencies shows that BSPT threaded fittings have an average lifespan that is 20-25% longer than NPT alternatives when subjected to normal operational stresses. This hard data underpins why UK standards like BS EN 10226-1 mandate their use in so many critical applications.
You can dive deeper into the data behind these UK standards and performance findings to understand the full regulatory context.
How to Reliably Identify NPT and BSPT Threads
Getting your threads mixed up is a classic, and often costly, mistake. But out in the field, telling NPT and BSPT threads apart is actually quite straightforward once you know what to look for. Forget the textbooks for a moment; a couple of quick visual checks and some simple measurements will save you from a catastrophic connection failure, especially when you're working with unmarked fittings or imported equipment.
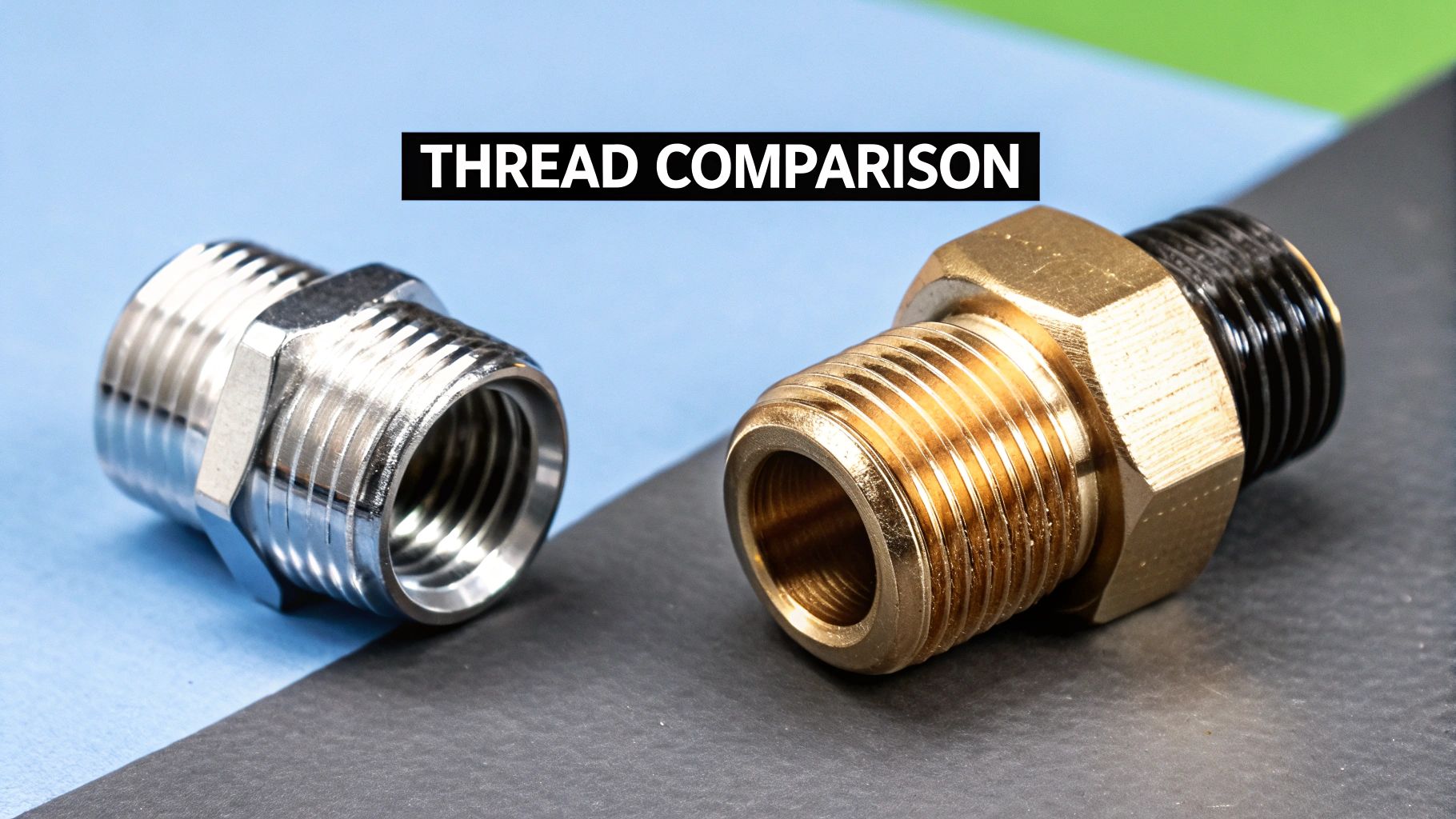
Your first move should always be a simple visual inspection. Look closely at the thread profile itself. NPT threads have distinct flattened crests and roots, which gives them a somewhat rugged, blocky appearance. By contrast, BSPT threads have a clearly rounded profile. This subtle curve is a dead giveaway and is often all you need to make a solid initial guess.
Using Tools for Positive Identification
For absolute certainty, you'll want to grab two basic tools: a set of calipers and a thread pitch gauge. These tools take all the guesswork out of the NPT vs. BSPT debate and give you a definitive answer.
Measure the Thread Angle: This is the most reliable tell-tale sign. A thread pitch gauge has blades marked with different angles. If you press a 60° gauge blade against an NPT thread, it will sit perfectly flush. Try that same blade on a BSPT thread, and you'll see daylight through the gaps. Now, switch to a 55° blade—it’ll nestle into the BSPT thread like it was made for it.
Determine the Pitch: Next, use the same gauge to figure out the threads per inch (TPI). Lay the different TPI blades against the thread until one meshes perfectly, with no rocking or gaps. While it's true that some NPT and BSPT sizes share a pitch (like 1/2" fittings, which are both 14 TPI), most don't, making this another great check.
Check the Diameter: Finally, use your digital calipers to measure the outside diameter (OD) of the male thread. For example, a 1/2" NPT fitting has an OD of roughly 21.3 mm, whereas its 1/2" BSPT counterpart is slightly smaller at around 21.0 mm.
Safety is Non-Negotiable: If you spot a mismatch, whatever you do, don't try to force the connection. The difference in angle and pitch guarantees it will leak under pressure, potentially causing serious damage. The only correct and safe solution is to use a purpose-built NPT to BSPT adapter.
Proper identification isn't just about getting the job done right; it's a fundamental part of workshop safety. Taking that extra minute to verify the thread type protects your equipment, prevents costly downtime, and ensures your system is secure and leak-free.
For a deeper look into the American standard, you can find more information about the specifics of NPT threads in our detailed guide.
Choosing the Right Thread for Your Application
Picking the correct thread is about much more than a simple NPT vs BSPT showdown. It’s a critical engineering choice that hinges on your specific application, where in the world you are, and what safety protocols you need to follow. The right decision will come down to factors like the system's operating pressure, the fluid or gas you're working with, and whether it has to endure heavy vibration.
For instance, across the UK and Europe, BSPT is the undisputed standard for hydraulics and pneumatics. Its 55° thread angle and clever metal-to-metal sealing design make it incredibly reliable under the high pressures these systems are known for. This gives it an inherent advantage, minimising the risk of leaks and making it the go-to choice for performance and safety in demanding industrial environments.
On the other hand, NPT is still king in North America for general-purpose industrial and plumbing jobs. Its simple, tough design is a good fit for lower-pressure water, air, and gas lines where relying on thread deformation and a bit of sealant is perfectly acceptable.
A Framework for Decision-Making
When you're trying to decide between the two, especially if you're mixing equipment from different parts of the world, use these points to guide you:
- Operating Pressure: If you're dealing with high-pressure hydraulics or pneumatics, BSPT is almost always the more reliable and safer bet because of its superior sealing method.
- Vibration Levels: In environments with a lot of vibration, like on heavy machinery, the precise fit of BSPT threads tends to provide a more durable and secure connection over time compared to NPT.
- Regulatory and Regional Compliance: This one isn't up for debate. If your project is in the UK or Europe, using BSPT isn't just a suggestion—it's often a legal requirement to ensure safety and system integrity.
Key Insight: The real question isn't about which thread is "better" in a vacuum. It's about which thread was specifically engineered for the demands and rules of your application. Choosing the wrong one is like introducing a deliberate and dangerous weak point into your entire system.
The UK Context: A Clear Preference for BSPT
Here in the UK, the choice is overwhelmingly clear. The deep-rooted adoption of BSPT is driven by decades of established engineering practice and strict safety regulations.
In fact, market data reveals that around 90-95% of all threaded pipe connections in UK plumbing, gas, and industrial systems are based on BSP or BSPT standards. This dominance is backed by regulatory bodies like the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), which often specifies BSPT fittings for pressurised pipelines to guarantee joint integrity and cut down on failure rates. A 2022 survey highlighted this, finding that a tiny 4% of pipe fittings used by UK manufacturing firms were NPT, and these were almost always found on imported equipment from North America. You can find out more about these consolidated screening standards and UK compliance.
Common Questions About NPT and BSPT Threads
Even after you get your head around the technical differences between NPT and BSPT, a few practical questions always seem to pop up. Let's clear up some of the most common points of confusion you'll likely face when working with these fittings.
The most frequent—and frankly, dangerous—question is whether you can just force an NPT fitting into a BSPT port. The answer is an emphatic no. It might feel like it's starting to thread, but the mismatched angles (60° for NPT, 55° for BSPT) and different pitches mean you'll never get a proper, safe connection. Forcing it creates a weak joint that's guaranteed to leak under pressure and will almost certainly ruin the threads on both parts. The only right way to connect the two is with a purpose-built NPT to BSPT adapter.
Sealant Use and Which Thread Is "Better"
Another area that trips people up is how to use sealants. With NPT threads, using a quality thread sealant paste or PTFE tape isn't optional; it's mandatory. The sealant's main job is to fill the tiny spiral gap inherent in the thread design, which is what actually creates the pressure-tight seal.
On the other hand, with BSPT threads, the primary seal comes from the precise metal-on-metal contact between the thread flanks. Here, any sealant you apply is really just acting as a lubricant to prevent the threads from galling or seizing when you tighten them. It also serves as a secondary backup against any minor imperfections.
So, is one thread type really better than the other? It all comes down to context. BSPT is often the go-to choice for high-pressure hydraulic systems, especially across the UK and Europe, thanks to its robust sealing design. NPT, however, is deeply rooted as the standard for general industrial and plumbing work all over North America.
Ultimately, the "best" thread is the one that's correct for your region, your specific application, and any regulations you need to follow. If you have more questions, our extensive Frequently Asked Questions section is packed with more insights.
At Solenoid Valve World, we provide the expertise and components you need to build safe and reliable fluid control systems. Explore our wide range of solenoid valves and fittings today.
