Steam Pressure Reducing Valve Guide for Smart Operations
Understanding Steam Pressure Reducing Valve Fundamentals
Steam is a powerful force in many industrial settings, but managing its raw energy is critical. The steam pressure reducing valve (PRV) plays a key role in this process. Think of it as a regulator, carefully controlling steam flow and pressure to meet the specific demands of various applications. This precise control is essential for both efficient operation and safety.
A steam PRV takes high-pressure steam from the boiler and reduces it to a lower, manageable pressure downstream. This isn't just about restricting flow; it's about maintaining consistent, stable pressure even when demand or upstream supply fluctuates. This consistency ensures processes run smoothly and equipment stays within safe operating limits.
Core Components and Functionality
A PRV's internal components are the key to its operation. A diaphragm or piston acts as the valve's sensor, detecting pressure changes and adjusting accordingly. This sensing element is connected to a valve seat and plug, which physically controls the steam flow. A spring provides the counteracting force, allowing the valve to fine-tune the pressure reduction. Some PRVs also incorporate a pilot valve for even more precise control in demanding situations.
Evolution of Valve Designs
The use of steam PRVs has a rich history, particularly in the UK, dating back to the late 19th century. This period coincided with significant advancements in steam technology during the Industrial Revolution. By the early 20th century, these valves were essential in various industrial processes, including steam heating systems. You can explore more about the history of steam pressure reducing valves here: Discover more insights
PRV designs have continually evolved since those early days. Materials have advanced from basic metals to more durable, corrosion-resistant alloys. Control mechanisms have also become more sophisticated, integrating advanced sensing and actuation technologies. These improvements have resulted in more reliable, efficient, and safe operation, meeting the demanding performance needs of modern industries. For instance, today’s PRVs can handle significantly higher pressure differentials and offer finer control over the reduced pressure.
Importance of Correct Valve Selection
Choosing the right steam PRV is crucial for optimal system performance. An incorrectly sized or specified valve can lead to pressure fluctuations, equipment damage, and even safety hazards. It’s like trying to control a powerful firehose with a garden tap—the results could be unpredictable and dangerous. Selecting the correct PRV ensures your steam system operates safely and efficiently. This selection process involves carefully considering factors such as inlet pressure, desired outlet pressure, flow rate, and the specific application requirements. Understanding these fundamentals will help you maximize the effectiveness of your steam system.
Choosing The Right Steam Pressure Reducing Valve Type
Selecting the correct steam pressure reducing valve (PRV) is essential for a well-functioning system. A variety of PRV types exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is the first step towards optimizing your steam system’s performance and ensuring it lasts.
Direct-Acting vs. Pilot-Operated Valves
Direct-acting PRVs are mechanically simpler. The downstream pressure directly impacts the diaphragm or piston, controlling the valve's opening and closing. This design is cost-effective and suitable for applications with smaller flow rates and less stringent pressure control needs. It's a direct, immediate response to pressure fluctuations.
Pilot-operated PRVs use a smaller pilot valve to control the main valve. This two-stage process allows for greater precision and responsiveness, especially with fluctuating loads. These valves are excellent for high-flow applications and where tight pressure control is critical. It’s a more refined, controlled response. You might be interested in: How to master pressure reducing valves.
Spring-Loaded vs. Diaphragm-Actuated Systems
Spring-loaded PRVs use a spring to counteract the steam pressure. These valves are robust and reliable, but their pressure control can be affected by changes in spring tension over time. They work well for stable pressure requirements.
Diaphragm-actuated PRVs use a flexible diaphragm to sense and respond to pressure changes. This design provides more responsive control and greater accuracy. Diaphragm-actuated valves are preferred for applications requiring precise pressure regulation and where inlet pressure may vary.
Specialized Valve Types: Self-Contained and Externally Piloted
Self-contained regulators house all necessary components within a single unit. This simplifies installation and maintenance. They are well-suited for smaller systems or specific pressure control points.
Externally piloted systems offer increased flexibility by separating the pilot valve from the main valve. This setup allows for remote control and tailored pressure regulation strategies.
To help you choose the best valve for your needs, the following table summarizes key differences between common steam PRV types:
Steam Pressure Reducing Valve Types Comparison
This table compares different valve types, highlighting their operating pressure ranges, capacity, ideal applications, and key advantages.
| Valve Type | Pressure Range | Capacity | Best Applications | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-acting | Lower | Lower | Smaller systems, stable loads | Cost-effective, simple design |
| Pilot-operated | Wider | Higher | Large systems, fluctuating loads | Precise control, responsive |
| Spring-loaded | Stable | Moderate | Constant pressure needs | Robust, reliable |
| Diaphragm-actuated | Variable | Moderate | Precise pressure regulation | Accurate, responsive |
| Self-contained | Varies | Varies | Smaller systems, localized control | Easy installation, compact |
| Externally piloted | Varies | Varies | Remote control, custom strategies | Flexible, adaptable |
This comparison helps illustrate the diverse capabilities of various PRV types, enabling you to select the optimal valve for your specific application. Consider your system's size, required pressure range, and desired level of control when making your decision.
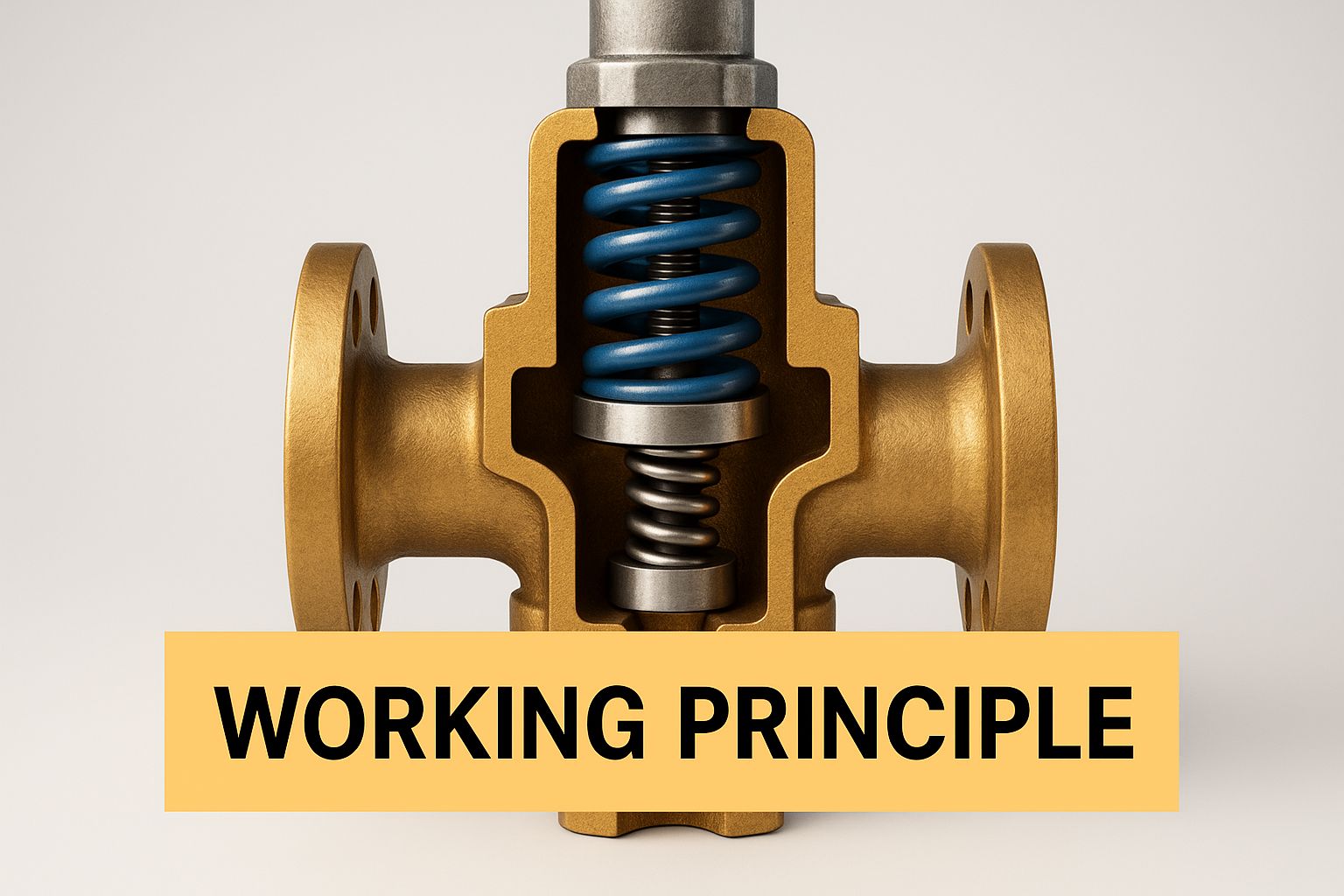
This infographic shows how a steam PRV works, highlighting the internal piston and spring mechanism. The image demonstrates how the piston reacts to pressure changes, adjusting the valve opening to maintain the desired downstream pressure. This mechanism is vital for stable steam pressure in various industrial applications.
Choosing the right steam PRV involves carefully considering several factors. These include the required pressure range, flow capacity, accuracy needs, and the specific application demands. Understanding these factors, along with the different valve types, will ensure optimal performance and a long lifespan for your steam system. This informed decision directly contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of your operations.
Maximizing ROI Through Strategic Steam Valve Applications
Smart deployment of steam pressure reducing valves (PRVs) is transforming operational efficiency across various UK industries. From chemical processing and food production to pharmaceuticals and textile manufacturing, leading facilities are using PRVs to achieve measurable cost reductions while enhancing process consistency. It's not just about better steam management; it's about a healthier bottom line.
Cost Savings Through Optimized Piping
One key advantage of incorporating steam PRVs is the ability to optimize piping systems. By precisely controlling downstream pressure, facilities can often use smaller diameter piping for steam distribution. This reduction in pipe size translates directly into lower material costs and reduced installation expenses. These savings can be substantial, especially in large industrial settings where cost-efficiency is a primary concern. Additionally, using steam PRVs allows for efficient steam delivery by minimizing the size of distribution piping. Discover more insights about steam distribution piping.
Enhanced System Reliability and Energy Efficiency
Strategic PRV implementation doesn't just save on initial setup; it contributes to long-term reliability and energy efficiency. Maintaining consistent pressure with PRVs minimizes wear and tear on downstream equipment. This reduces maintenance costs and prevents costly downtime. Furthermore, precise pressure control optimizes steam usage, leading to significant energy savings and a smaller carbon footprint. This translates to lower operating costs over time.
Practical Applications Across Industries
The benefits of steam PRVs are evident across a range of applications.
- Food Processing: Precise temperature control facilitated by PRVs is crucial for maintaining product quality and preventing spoilage.
- Textile Manufacturing: Consistent steam pressure ensures uniform dyeing and finishing processes.
- Pharmaceutical Production: Meticulously controlled steam is often essential for sterilization and other critical processes.
- District Heating: PRVs play a vital role in ensuring efficient and reliable heat distribution to multiple buildings.
These examples showcase the versatility and impact of steam PRVs across diverse industrial settings in the UK.
Quantifiable Results and Improved Bottom Line
The impact of strategic steam PRV application is measurable. Case studies across various sectors demonstrate operational improvements and energy savings that directly affect profitability. By reducing steam waste, optimizing piping systems, and improving equipment reliability, facilities see a demonstrable return on their PRV investment. These improvements ultimately contribute to greater operational efficiency and enhanced profitability for UK businesses.
Navigating UK Compliance For Steam Pressure Reducing Valves
Ensuring your steam pressure reducing valves (PRVs) meet UK regulations is critical for safe and efficient operations. This means understanding and following relevant British Standards, Health and Safety Executive (HSE) guidelines, and the Pressure Systems Safety Regulations (PSSR). Overlooking these regulations can result in significant penalties and, more importantly, jeopardize safety.
British Standards and HSE Guidelines
Several British Standards address PRV installation and maintenance, offering detailed specifications for safe operation. These standards, frequently cited in HSE guidelines, provide best practices for valve selection, installation, and testing. Adhering to these guidelines is key for demonstrating due diligence and upholding a safe working environment.
PSSR Requirements for PRVs
The PSSR forms a cornerstone of UK pressure systems safety legislation. This regulation outlines specific requirements for the installation, operation, and maintenance of pressure systems, including those with PRVs. This necessitates regular inspections by a competent person. Maintaining detailed records of these inspections is also mandatory, creating an auditable compliance trail.
Mandatory Inspections and the Competent Person
Regular inspections, performed by a designated competent person, are essential for PSSR compliance. This individual must possess the requisite skills, knowledge, and experience to evaluate the PRV's safety and integrity and its associated pressure system. This ensures prompt identification and resolution of potential issues, minimizing incident risk. Proper documentation of these inspections is also crucial.
Historical Context and Regulatory Development
The development of steam technology, including PRVs, in the UK has been shaped by broader industrial and safety standards. The focus on safety and efficient steam management paved the way for more advanced technologies like pressure reducing valves. Learn more about safety valve history
Certification and Ongoing Compliance
Achieving UK compliance often involves obtaining certifications for your PRVs and pressure systems. These certifications validate adherence to relevant standards and provide assurance of safe operation. Maintaining ongoing compliance requires proactive measures, including regular maintenance, inspections, and up-to-date documentation. Learn more in our article about UK electrical supply voltages You might also find this interesting: social media ROI.

By following these compliance measures, UK facilities can ensure the safe and efficient operation of their steam systems, minimizing risks and maximizing the advantages of pressure reducing valves. Ultimately, compliance fosters a safer and more productive work environment.
Installation Best Practices That Prevent Costly Failures
Proper steam pressure reducing valve (PRV) installation is crucial for a reliable steam system. A well-installed PRV contributes to efficient operation, while a poorly installed one can lead to costly maintenance, headaches, and even system failures. This section covers the best practices that ensure long-term performance and cost savings.
Upstream and Downstream Piping Requirements
Correct piping configuration is fundamental to PRV performance. A drip leg and steam trap installed upstream of the PRV are essential for removing condensate. This prevents water hammer, which can damage the valve and other system components. Downstream, a pressure gauge is necessary for monitoring and adjusting the reduced pressure, ensuring it meets the requirements of your application.
Installing a strainer upstream protects the PRV from debris and particulate matter. This is particularly important for pilot-operated PRVs, which have small clearances that can be easily blocked. A bypass line with a globe valve allows for isolating the PRV for maintenance or replacement without shutting down the entire steam system. This bypass is critical for minimizing disruption during maintenance.
Insulation and Bypass Arrangements
Insulation plays a key role in maintaining steam quality and preventing energy loss. Properly insulating the piping around the PRV minimizes heat loss and keeps the steam dry, improving system efficiency and reducing operating costs. The bypass arrangement discussed above also requires proper consideration. The globe valve within the bypass allows for throttling the steam flow, useful for fine-tuning pressure during maintenance.
Valve Sizing and Pressure Drop Considerations
Accurate valve sizing is paramount. An oversized valve will struggle to control pressure effectively, leading to fluctuations and potential damage to downstream equipment. Undersized valves restrict flow and may not meet the demands of the application. Calculating the required valve capacity involves considering factors like inlet pressure, desired outlet pressure, and the expected flow rate, measured in lbs/hr.
Understanding pressure drop is also crucial. PRVs require a minimum pressure drop across the valve to function correctly. Ensure your system design provides this minimum differential, often around 20%. Failing to account for this can lead to inaccurate pressure control and potentially damage the PRV. Remember, there is a maximum pressure reduction ratio (usually 10:1) from inlet to outlet.

This image illustrates a typical PRV installation, highlighting key components like the strainer, drip leg, and bypass line. It demonstrates how these elements work together for efficient and reliable operation.
Condensate Management and Commissioning
Effective condensate management is vital. Accumulated condensate can disrupt pressure control and damage the PRV. Properly sized and positioned steam traps are essential for promptly removing condensate. Thorough system commissioning ensures proper installation and functionality.
During commissioning, verify the pressure settings, check for leaks, and ensure the bypass is working correctly. This final check confirms the PRV and related components are operating as intended, preparing the system for long-term reliable service.
Proven Maintenance Strategies For Steam Valve Reliability
Maintaining your steam pressure reducing valves (PRVs) is essential for reliable operations and preventing costly downtime in your UK facility. A well-maintained PRV can significantly extend its lifespan. Conversely, neglecting maintenance can lead to unexpected failures and expensive emergency repairs.
Preventive Maintenance Schedules
A robust preventive maintenance schedule is the first step towards PRV reliability. This schedule should be tailored to your specific operating conditions and the manufacturer's recommendations.
For instance, a PRV operating under high pressure and temperature fluctuations may require more frequent inspections than one in a more stable environment. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential problems early, preventing them from becoming major issues.
Inspection Techniques for Early Problem Detection
Regular inspections are crucial for identifying potential issues before they impact operations. These inspections should include checks for several key indicators.
- External Leaks: Look for any signs of steam leakage around the valve body, bonnet, or packing gland. Address these leaks promptly.
- Internal Leaks: A gradual increase in downstream pressure when the system is idle can point to an internal leak.
- Unusual Noises: Hissing or chattering sounds may signal problems with the valve seat or internal components.
- Pressure Hunting: Wide fluctuations in downstream pressure often suggest issues with the control mechanism.
Early detection through these regular inspections can save you thousands of pounds in potential emergency repair costs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
PRVs can experience a variety of problems. The following table provides a quick troubleshooting guide, outlining common symptoms, their likely causes, immediate solutions, and preventive measures.
This table, "Common Steam Pressure Reducing Valve Problems and Solutions," offers a troubleshooting guide showing symptoms, likely causes, recommended solutions, and prevention methods to keep your system running smoothly.
| Symptom | Likely Cause | Immediate Solution | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Downstream Pressure | Damaged diaphragm | Replace diaphragm | Regular inspection |
| High Downstream Pressure | Leaking valve seat | Re-lap or replace seat | Strainer installation upstream |
| Pressure Hunting | Incorrectly sized valve | Adjust or replace valve | Proper sizing calculations |
| Capacity Reduction | Blocked strainer | Clean or replace strainer | Regular strainer maintenance |
These troubleshooting tips offer practical, immediate solutions and long-term preventative measures, helping you avoid costly repairs or premature valve failures.
Valve Rebuild vs. Replacement
When a PRV malfunctions, you'll need to decide whether to rebuild or replace it. Rebuilding involves replacing worn parts like the seat, diaphragm, or seals, which can be cost-effective for minor issues.
However, for extensive damage or if the valve is nearing the end of its expected lifespan, replacement offers a more sensible long-term solution. Consistent maintenance and inspection will help you make informed decisions about rebuilding versus replacement.
Spare Parts Inventory Management
Maintaining an inventory of essential spare parts, such as diaphragms, seals, and springs, can significantly reduce downtime. Having these parts on hand allows for faster repairs, minimizing disruptions to your operations.
For less common or specialized PRV models, establishing a reliable supplier relationship is crucial for quick access to the components you need. This proactive approach to parts management can save valuable time and resources.
By implementing these maintenance strategies, you can maximize the lifespan of your steam pressure reducing valves, minimize downtime, and improve your overall steam system's reliability. This proactive approach will save you money in the long run and ensure consistent and efficient operation.
Smart Technology Trends In Steam Pressure Reducing Valves
The world of steam pressure reducing valves (PRVs) is constantly evolving. Advancements in materials science, digital monitoring, and predictive maintenance are driving this change. These innovations offer tangible benefits for UK facilities, improving efficiency, lowering operational costs, and enhancing safety.
Smart Valves with Integrated Sensors
Modern PRVs are getting smarter. Smart valves now include integrated sensors that provide real-time data on pressure, temperature, and flow rate. This data gives valuable insights into system performance, allowing for precise control and optimization.
For example, a smart valve can automatically adjust its operation based on real-time demand. This ensures optimal pressure stability while minimizing energy waste, a level of control impossible with traditional mechanical valves.
Remote Monitoring and Predictive Analytics
Entire steam systems are becoming more connected. Remote monitoring systems allow engineers to supervise PRV performance from anywhere, providing instant alerts for potential issues. This rapid response capability prevents costly downtime.
Predictive analytics leverages this data to forecast potential failures. This allows for proactive maintenance scheduling, saving time and resources. For maintaining steam pressure reducing valves, consider the general guidelines for equipment maintenance.
Advanced Materials and Industry 4.0 Integration
New materials are playing a significant role in PRV evolution. High-performance alloys and composites offer improved durability and corrosion resistance in challenging environments. This extends valve lifespan and reduces maintenance needs.
Industry 4.0 principles, through IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity and data-driven insights, are transforming valve operation. This interconnectedness creates new possibilities for optimization and efficiency. The Fisher Controls Company introduced significant improvements in steam pressure regulation, showcasing the impact of steam technology on industrial processes. Explore this topic further. You can also find helpful information on how to find the right steam valves.
By embracing these trends, UK facilities can significantly improve steam system efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. These innovations represent a fundamental shift in how steam systems are managed and optimized.
Upgrade Your Steam System with Solenoid Valve World
Ready to optimize your steam system with advanced valve technology? Visit Solenoid Valve World today. Explore our range of high-quality solenoid valves, pressure control equipment, and expert advice tailored for UK businesses. Our expert team can help you select the right valve for your application, ensuring efficient operation and regulatory compliance.
