Understanding BSP Thread Size and Its Importance in Solenoid Valves for Optimal Performance
Introduction to BSP Thread Size:
When it comes to industrial applications, solenoid valves are essential components used for controlling the flow of fluids and gases. Whether you're in the field of automation, pneumatics, or hydraulics, understanding the right fittings for solenoid valves is crucial for ensuring optimal functionality. One critical aspect of solenoid valve fittings is the **BSP thread size**.
BSP (British Standard Pipe) thread sizes are commonly used in a variety of applications, and their proper selection is vital for leak-free, durable installations. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of BSP thread sizes in solenoid valves, how to select the correct size, and why it matters for the performance and longevity of your solenoid valve systems.
What is BSP Thread Size?
BSP is a family of standard thread types used for connecting pipes and fittings. The two most common types of BSP threads are:
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel): These threads are used for applications where the connection is not tapered and relies on a flat seal for sealing.
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered): These threads are tapered and used in applications where the pipe and fitting seal against each other via the threads themselves.
The BSP thread size is a standard used internationally, particularly in Europe, and is widely compatible with many different pipe systems, including water, gas, and oil systems.
Why is BSP Thread Size Important in Solenoid Valves?
When installing solenoid valves in any piping system, the thread size of the valve connections is crucial for the following reasons:
1. Leak Prevention: Properly sized BSP threads create a tight seal between the valve and the piping system. An incorrect size can lead to leaks, which can compromise the integrity of your system and potentially lead to safety hazards or operational inefficiencies.
2. System Efficiency: Using the correct BSP thread size ensures that the solenoid valve functions at optimal pressure and flow rates. Misalignments due to improper threading can restrict flow or cause pressure drops, negatively impacting system performance.
3. Durability: Solenoid valves are often used in harsh environments. An incorrect BSP thread size can lead to wear and tear on both the valve and the pipe connection, reducing the lifespan of both components and increasing maintenance costs.
4. Compatibility: BSP threads are widely used across various industries, and selecting the right size guarantees compatibility with other equipment and fittings. This simplifies the installation process and ensures that the system is unified in terms of thread standards.
How to Choose the Right BSP Thread Size for Your Solenoid Valve
Choosing the right BSP thread size for your solenoid valve involves considering several factors to ensure proper fitment and optimal performance:
1. Know the Valve’s Connection Type
Male or Female Threads: Solenoid valves typically feature either male or female BSP threads. You need to match the valve’s connection type with the appropriate fitting (male to female, or vice versa) in your piping system.
Parallel or Tapered Threads: Determine if the valve has BSPP or BSPT threads. For a BSPP fitting, you’ll need a matching BSPP fitting (with an O-ring or flat sealing surface). For BSPT, the sealing is done by the threads themselves, creating a tighter seal.
2. Size Specification
BSP thread sizes are usually defined by the diameter of the pipe (e.g., 1/8", 1/4", 1/2", 1", etc.) and the pitch of the threads. For example, a BSPT 1/2" thread has a nominal pipe size of 1/2 inch, with a specific thread pitch.
When selecting the right size:
Measure the pipe’s outer diameter to match it with the valve’s port size.
Pay attention to the system’s pressure and flow rate to ensure the chosen thread size can handle the conditions effectively.
3. Pressure and Temperature Ratings
Solenoid valves often operate in pressurized environments or extreme temperatures. Make sure the BSP thread size you select corresponds to the pressure and temperature requirements of your system. Larger diameters typically handle higher flow rates and pressures better.
Common BSP Thread Sizes Used in Solenoid Valves
Below are some of the most commonly used BSP thread sizes for solenoid valves:
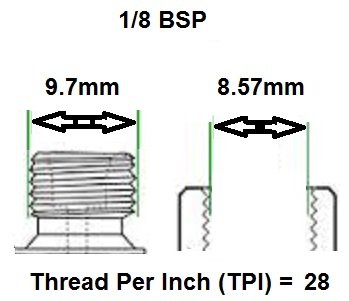
1/8 BSP: Suitable for low-flow applications, such as controlling small volumes of air or gas.
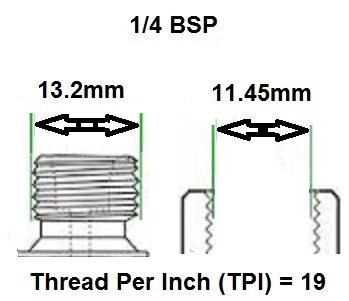
1/4 BSP: Common in small solenoid valves used for medium to low flow systems.
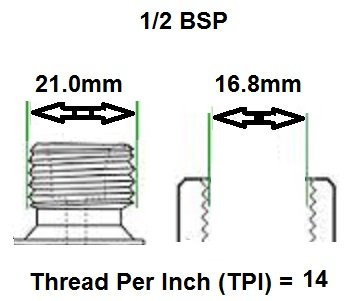
1/2 BSP: Ideal for standard solenoid valves in most industrial applications, including water or gas control systems.
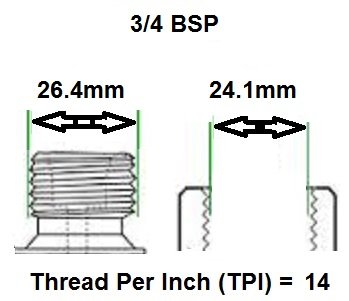
3/4 BSP: For higher flow applications, where larger solenoid valves are required for handling greater volumes of fluid or gas.
1 BSP: Typically used in large-scale industrial systems for controlling significant volumes of media.
Find valves by thread size here.
Key Considerations When Installing Solenoid Valves with BSP Threads
1. Sealing Methods:
For BSPP threads, you’ll likely use an O-ring or a flat dowty bonded seal to ensure leak-tight connection.
For BSPT threads, the sealing occurs as the tapered threads create a tight, frictional fit. Ensure proper tightening to prevent leaks, but avoid over-tightening, which could damage the threads.
2. Thread Lubrication:
Depending on the environment, thread lubrication can help prevent damage and wear over time, particularly in high-pressure systems. Ensure that the lubricant used is compatible with the medium being controlled.
3. Correct Torque Settings:
Over-tightening or under-tightening can both cause issues. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s recommended torque settings for the solenoid valve to ensure proper sealing and avoid damage.
4. Regular Maintenance:
Over time, BSP threads can wear down, especially under harsh operating conditions. Regular maintenance checks, including visual inspections and leak tests, will help prolong the life of the valve and the piping system.
In industrial systems, solenoid valves with the right BSP thread size play a critical role in ensuring efficient, leak-free operation. Proper selection and installation of the correct BSP thread size are key to avoiding operational failures, maintaining system efficiency, and extending the lifespan of both the solenoid valve and the overall piping system.
By understanding BSP thread sizes and following proper installation practices, you can optimize your solenoid valve’s performance, avoid costly downtime, and ensure that your system operates reliably under the most demanding conditions.
Always consult with technical experts or manufacturers for detailed specifications and advice on BSP thread sizes suited to your specific solenoid valve applications.
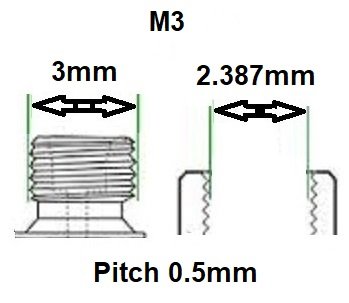
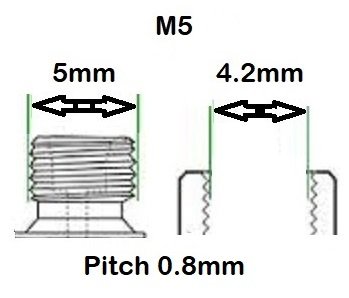
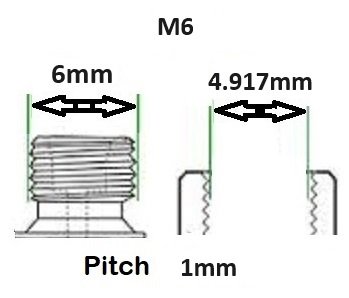
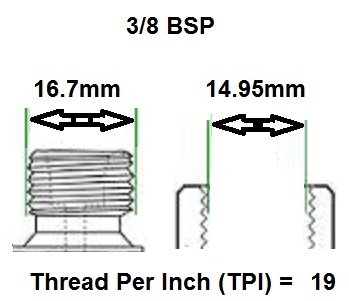
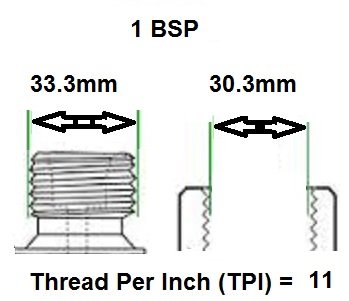
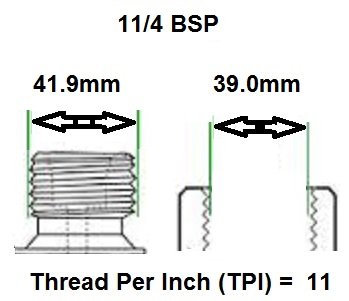
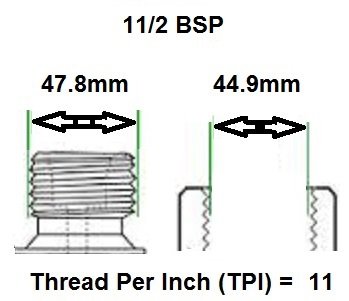
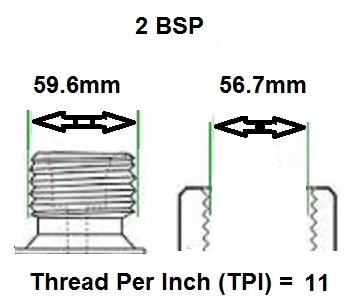
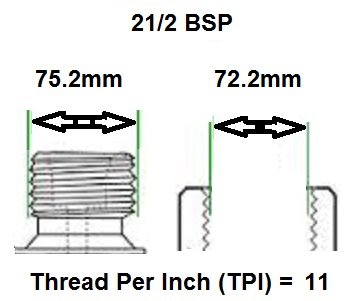
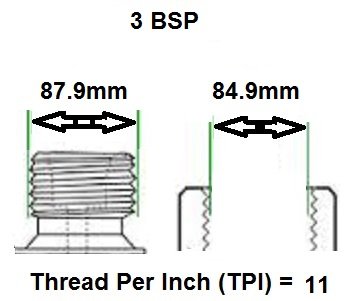
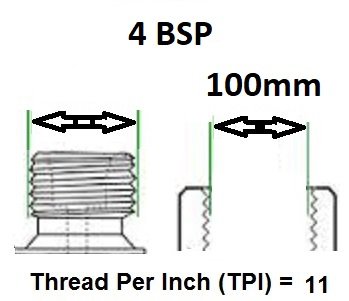
BSP thread size guide, including threads per inch (TPI) for Male BSP and Female BSP threads.