Excess Flow Valve Guide: UK Safety Systems That Save Lives
Understanding What Makes Excess Flow Valves Your First Line of Defence
Excess flow valves (EFVs) are vital safety components in UK gas systems. They act as a crucial first line of defence against potential hazards. These clever mechanisms work on a simple principle: they detect unusual gas flow and quickly shut off the supply. This prevents catastrophic events like explosions and fires. This rapid response is essential for minimizing the risks associated with gas leaks.
How EFVs Work: A Simple Analogy
Imagine a garden hose with a special valve. Water flows freely under normal conditions. But if the hose bursts, the increased water flow activates the valve to close, preventing further water loss. An EFV functions similarly, constantly monitoring gas flow. It reacts instantly to any significant increase, effectively "shutting off the hose" if a pipe ruptures or another system failure occurs.
Different Designs for Different Needs
Just as there are different types of garden hoses for various tasks, there are different EFV designs for specific applications. Spring-loaded models are common, using a spring's force to close the valve when a pre-set flow rate is exceeded. For more complex situations, pressure-differential systems offer greater precision by monitoring the pressure difference across the valve. Selecting the right design is crucial for optimal performance and safety.
Excess Flow Valves are used in various applications, including gas distribution systems. They're critical for preventing excessive gas flow if a pipe ruptures, reducing the risk of explosions and fires. In the UK, similar safety considerations require the use of EFVs to comply with stringent safety regulations. The Fisher F Series excess flow valves, for instance, are engineered to close upon excessive discharge of vapor or liquid, demonstrating their effectiveness in preventing accidents.
Real-World Success Stories: Preventing Disaster
The true value of EFVs lies in their proven ability to prevent disasters. Countless incidents have been avoided across the UK thanks to these devices. If you're looking for proactive solutions, check out this Expert Technical Troubleshooting Guide: Quick Fixes. Imagine a gas pipe damaged during construction. Without an EFV, the escaping gas could quickly create an extremely dangerous situation. However, with an EFV installed, the sudden increase in gas flow would immediately trigger the valve to close, preventing a potentially catastrophic gas build-up.
Modern Advancements: Reducing False Triggers
While speed and reliability are essential, modern EFV technology also focuses on reducing false triggers. Advanced algorithms and refined mechanical designs minimize the chances of the valve closing unnecessarily due to minor gas flow fluctuations. This ensures the system remains operational while maintaining its critical safety function. This balance between responsiveness and accuracy showcases the ongoing improvements in EFV technology.
Navigating UK Regulations That Actually Matter for Your Business

Understanding UK regulations concerning excess flow valves (EFVs) is critical for businesses in the gas industry. This isn't about paperwork overload; it's about focusing on the key safety requirements impacting your EFV choices. By examining the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) guidelines and the Gas Safety (Installation and Use) Regulations 1998, we can determine how EFVs contribute to your overall compliance strategy.
Mandatory vs. Recommended: Where EFVs Fit In
Understanding the distinction between mandatory EFV installation and recommended applications is crucial. Regulations differ based on the setting – residential, commercial, or industrial. New residential builds may mandate EFV installation on gas service lines, while older properties might not. Commercial and industrial settings have their own nuances, often based on the potential incident scale. Staying informed about regulations is vital. This requires a clear understanding of the specific regulations applicable to your business operations. You can learn more about general regulatory compliance for banks for context, though the specifics will differ for the gas industry.
Learning From Real-World Enforcement
Understanding how regulations are enforced in practice is key. Examining actual enforcement cases and inspection reports provides valuable insights into what regulators prioritize during safety audits. This proactive approach helps avoid penalties and fosters a safety culture within your organization. It also highlights areas where exceeding minimum requirements enhances safety and minimizes risk. This includes proper documentation, valve maintenance records, and adherence to testing procedures.
Practical Advice From The Field
Learning from experienced gas engineers who have navigated compliance challenges provides invaluable practical advice. They can offer insights into documentation requirements and effective communication with regulatory bodies. For example, maintaining organized records of EFV installations, maintenance, and testing is crucial for inspections. This demonstrates your commitment to compliance and ensures a smooth audit process.
Speaking of preventative measures, EFVs are vital for preventing gas leaks. In the United States, the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) mandates EFV installation in new and replacement gas service lines for single-family residences under the Pipeline Integrity, Protection, Enforcement, and Safety (PIPES) Act of 2006, implemented after June 1, 2008. Learn more about these regulations. While UK specifics may differ, similar safety concerns likely underpin UK regulations, emphasizing the vital role of EFVs in accident prevention.
UK Standards vs. International Best Practices
Finally, comparing UK standards to international best practices is essential. This broader perspective helps assess whether current regulations adequately protect your operations. It also informs decisions on voluntary upgrades to enhance safety and demonstrate a commitment to best-in-class practices. Exceeding minimum regulatory requirements can provide long-term benefits in safety and operational efficiency. For example, investing in higher-quality EFVs or more frequent testing could minimize costly incidents and downtime.
Choosing The Right Valve Without Costly Mistakes
Selecting the incorrect excess flow valve (EFV) can lead to significant expenses and compromise safety. This section explores crucial factors that influence EFV effectiveness in UK applications, incorporating insights from experienced engineers and safety professionals.
Sizing Your Valve for Optimal Performance
Accurately sizing your EFV is essential. An undersized valve restricts normal flow, hindering system performance. Conversely, an oversized valve may not react quickly enough during an emergency. Calculating the correct valve size requires understanding your system's typical flow rate, peak flow demands, and the acceptable pressure drop across the valve. Balancing sensitivity with the risk of false activation is also vital. For instance, a valve that's too sensitive might close due to minor flow surges, causing unnecessary disruptions.
Material Matters: Durability and Compatibility
The valve material significantly impacts its lifespan and effectiveness. In harsh environments with corrosion or extreme temperatures, a durable material like stainless steel is crucial. Consider an EFV in a coastal area exposed to salt spray. Corrosion-resistant materials ensure long-term reliability and prevent premature failure. Evaluating the specific operating conditions is paramount for proper material selection. You might be interested in: How to master solenoid valves for water.
Flow Rate, Pressure, and Installation: The Practical Considerations
Several practical considerations influence valve performance. Precise flow rate calculations are fundamental to proper sizing. Pressure ratings must meet or exceed system pressures for safe operation. Installation constraints, such as space limitations and pipe configuration, can also impact the choice of valve type and orientation. Careful planning prevents costly rework and ensures optimal valve function.
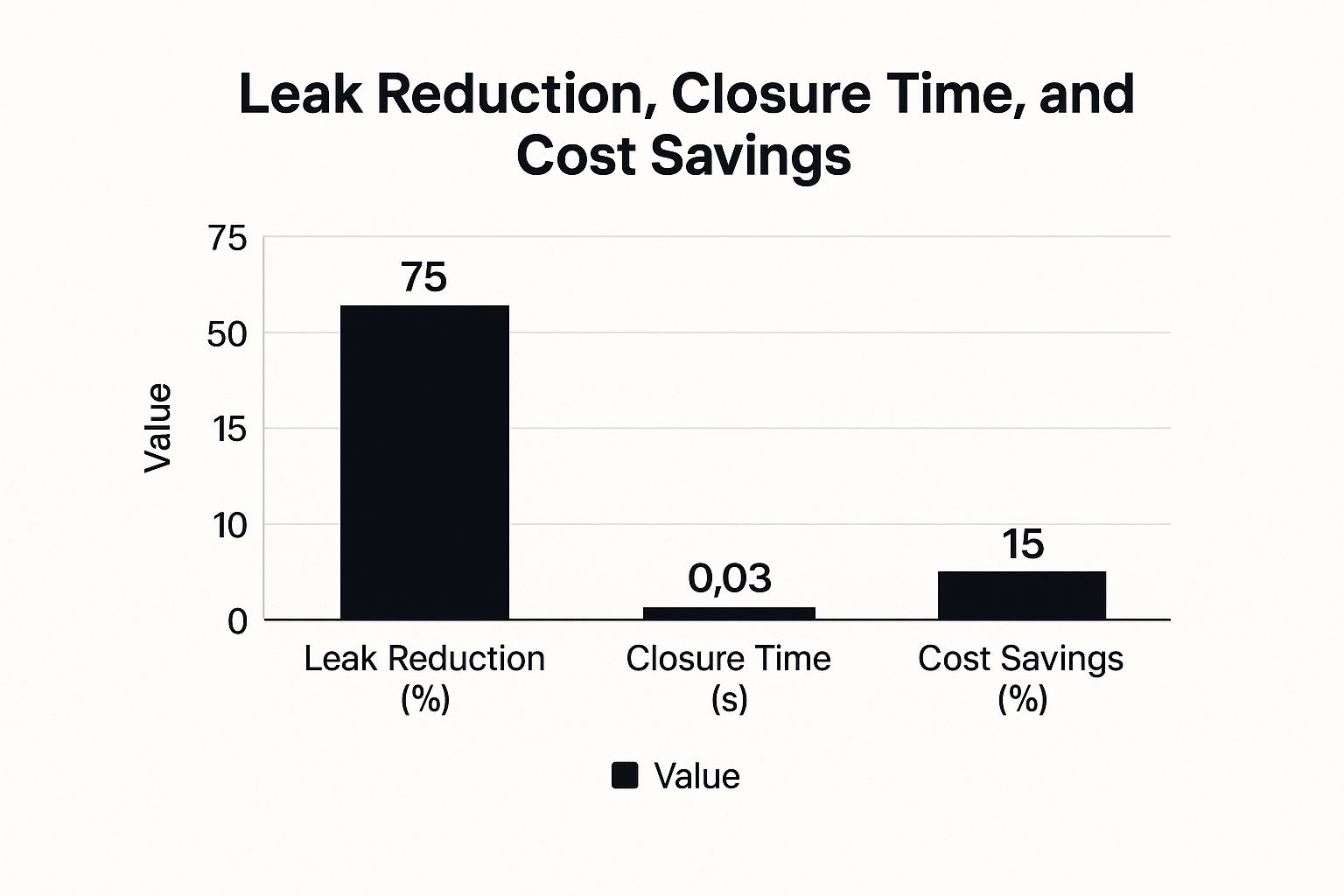
This infographic illustrates the key performance data of well-chosen excess flow valves, including leak reduction, closure time, and cost savings. The data highlights substantial benefits: a 75% leak reduction, a rapid 0.03-second closure time, and a 15% cost saving. These impressive results emphasize the significance of selecting the appropriate EFV.
To further clarify the various EFV options available, the following table provides a detailed comparison:
EFV Types and Applications Comparison
This table compares different excess flow valve types, their specifications, and suitable applications, helping you make an informed decision.
| Valve Type | Flow Rate Range | Pressure Rating | Best Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal | Low to Medium | Low to Medium | Residential gas lines | Cost-effective, simple installation |
| Piston | Medium to High | Medium to High | Industrial gas systems | Durable, accurate flow control |
| Spring-Loaded | Low to High | Low to High | Liquid and gas systems | Versatile, adjustable flow rate |
This comparison highlights the varying strengths of different EFV types, allowing for a more tailored selection process based on specific application requirements. Choosing the correct valve type based on these factors can significantly improve system efficiency and safety.
Emerging Technologies: Future-Proofing Your Safety
The field of excess flow valves is constantly evolving. Smart EFVs with remote monitoring capabilities are transforming gas system management. These advancements enable predictive maintenance and provide real-time performance tracking. New materials are extending service life, and design improvements minimize false activations. Integration with comprehensive safety management systems is also increasing. These developments offer opportunities to enhance safety and reduce maintenance needs. Choosing the right valve now involves considering current needs and future-proofing your system against evolving safety regulations and technological advancements.
Installation And Maintenance That Actually Works

Choosing the correct excess flow valve (EFV) is crucial, but proper installation and maintenance are equally important for these safety devices to function effectively. This section offers practical advice from engineers with extensive experience installing thousands of EFVs across various UK applications. For further information, check out this resource on valve installation and maintenance.
Avoiding Common Installation Pitfalls
Even small installation errors can impact an EFV's performance. Orientation is key; installing an EFV backward can prevent it from closing during an over-flow event. Pipe support is also critical. Insufficient support can strain valve connections, causing leaks or failures. Lastly, using the wrong sealing materials can lead to leaks or damage. Use PTFE tape sparingly on threaded connections, as over-tightening can crack the valve body.
Best Practices for Optimal Placement and Orientation
Excess flow valves should be installed in accessible locations for easy testing and maintenance. This allows for quick isolation and routine checks. Correct orientation is essential. The flow arrow on the valve body must align with the gas flow direction to ensure proper internal operation. Supporting pipework on both sides of the valve with appropriate hangers minimizes stress and prevents potential issues.
Testing Your Installation: Ensuring Proper Operation
Testing after installation is crucial. Simulate an excess flow by quickly opening a downstream valve. This should trigger the excess flow valve to close. Accurate interpretation of the results is important. If the valve closes slowly or incompletely, investigate for obstructions, incorrect sizing, or valve mechanism damage.
Developing a Realistic Maintenance Schedule
Regular maintenance is essential for long-term EFV reliability. Create a schedule based on your specific operating conditions, including gas type, pressure, and environment. Harsh environments, like coastal areas with high salt content, may require more frequent inspections for corrosion.
Recognizing the Warning Signs and Taking Action
Be aware of early warning signs of excess flow valve problems. Slower closure times or minor leaks can indicate developing issues. Regular visual inspections and performance tests can identify potential problems. When replacement is needed, choose a compatible valve, matching the original specifications or considering newer models with enhanced features.
Record-Keeping and Building Relationships
Detailed records of installation, testing, and maintenance are essential for compliance and troubleshooting. These records provide valuable documentation during inspections and track performance history. A strong relationship with a qualified service provider is invaluable. They can provide expert advice, troubleshoot issues, and offer prompt repairs or replacements, minimizing downtime and ensuring optimal EFV performance.
Smart Technology Trends Transforming EFV Performance

The excess flow valve (EFV) industry is constantly changing, driven by advancements in digital technology and ever-increasing safety regulations. This progress brings exciting new ways to improve gas system management in the UK. This section will explore the main trends shaping the future of EFV technology and their impact on businesses.
Remote Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
Smart EFVs, equipped with remote monitoring capabilities, are revolutionizing how we manage gas systems. These devices transmit real-time data on flow rates, pressure, and temperature. This provides valuable insights into system performance, allowing for predictive maintenance.
Identifying potential issues before they become major failures is a key advantage. For example, a small rise in pressure drop across the valve could suggest a partial blockage. This allows for timely intervention, preventing a complete shutdown. Learn more about managing vacuum systems with vacuum solenoid valves. This proactive approach reduces downtime and minimizes the risk of expensive incidents.
Enhanced Materials and Design: Longer Life, Fewer False Activations
Materials science is crucial for improving EFV performance. New materials offer better resistance to corrosion and extreme temperatures. This increases service life and reliability in challenging environments.
Combined with innovative designs, these advances also result in fewer false activations. For instance, advanced algorithms can differentiate between true excess flow events and minor fluctuations. This ensures the valve activates only when genuinely necessary, minimizing disruptions.
Integration with Broader Safety Management Systems
Modern EFVs are increasingly integrated with larger safety management systems. This allows for centralized monitoring and control, streamlining safety procedures and providing a complete overview of system health.
Data from the EFV can be combined with information from other sensors and systems. This enables a more thorough risk assessment and facilitates coordinated responses to emergencies. This integration simplifies safety management and strengthens overall system resilience.
The Expanding Global EFV Market
The global market for excess flow valves is seeing significant growth. While specific UK data may be limited, global trends show a rising demand for EFVs. This is due to their vital role in safety and efficiency across numerous industries. The global excess flow valve market is projected for significant expansion by 2031. Find more detailed statistics here. This highlights the growing global recognition of these important safety devices.
Early Adopters and The Challenges of Upgrading
Early adopters of new EFV technology are already experiencing the advantages: reduced maintenance costs, improved safety, and increased operational efficiency. However, upgrading older systems can be difficult.
Retrofitting existing systems with smart technology can be complex and requires careful planning. Compatibility problems with current infrastructure and the need for specialized staff training can also pose challenges. Carefully evaluating the benefits and difficulties of upgrading is vital for sound investment decisions.
Balancing Investment and Maintenance: A Forward-Looking Approach
Deciding between maintaining current equipment and investing in new technology involves several factors. The age and condition of existing EFVs, the possibility of integration with new systems, and long-term operational goals are all important.
Taking a proactive approach allows businesses to balance investment costs against the long-term operational advantages. This helps ensure safety systems remain both effective and budget-friendly. The ultimate goal is to maintain a strong, reliable safety system that protects both personnel and valuable assets.
Solving Problems Before They Become Emergencies
Even the most reliable excess flow valves (EFVs) can occasionally malfunction. Promptly addressing these issues is vital for maintaining a safe gas system. This guide offers practical advice for UK gas professionals, based on real-world scenarios, to troubleshoot common EFV challenges.
Diagnosing EFV Issues: A Systematic Approach
A systematic approach helps pinpoint the root cause of EFV problems, whether due to valve defects, installation errors, or system conditions leading to false activations. Begin by visually inspecting the valve for obvious signs of damage, such as leaks or cracks in the valve body.
Next, verify that both the gas supply pressure and flow rate are operating within the EFV's specified range. Discrepancies here can lead to unexpected behavior. Finally, thoroughly test the valve's activation mechanism. Simulate excess flow conditions to confirm the valve responds correctly.
Common Problems and Solutions: A Practical Guide
The following table summarizes frequent EFV issues, their associated symptoms, potential causes, and recommended solutions. It serves as a quick reference for gas professionals when troubleshooting in the field.
To help understand and resolve common issues, we've compiled a comprehensive troubleshooting guide:
Common EFV Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Symptoms | Likely Causes | Recommended Action | Prevention Tips |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| False Activation | Valve closes unexpectedly during normal operation. | Overly sensitive setting, pressure fluctuations in the system, debris trapped in the valve. | Check the valve setting, inspect the system for pressure irregularities, clean the valve internals. | Ensure correct valve sizing, install a pressure regulator upstream, implement regular maintenance. |
| Slow Closure | Valve closes slowly during an excess flow event. | Weak spring, internal component wear, blockage in the valve. | Replace the spring, repair or replace worn components, clear any blockages. | Regular maintenance and inspection, use of compatible gas types. |
| Leakage | Gas leak around the valve body or connections. | Damaged seals, loose fittings, corrosion. | Replace seals, tighten fittings, address corrosion issues. | Use appropriate sealing materials, proper installation techniques, regular inspection for corrosion. |
| Failure to Close | Valve doesn't close during an excess flow event. | Mechanical failure, incorrect installation, blockage. | Investigate the valve mechanism, check installation orientation, remove any blockages. | Regular testing and maintenance, proper installation procedures. |
This table provides a practical starting point for addressing common EFV issues, enabling swift resolution and minimizing potential hazards. Regular inspection and maintenance are key to preventing these issues.
Emergency Procedures: Handling Unexpected Valve Activation
If an EFV activates unexpectedly, a calm and systematic response is essential. The first step is to shut off the main gas supply, isolating the affected area. This prevents further gas flow and potential risks.
Next, investigate the reason for the activation. Determine whether it was a legitimate excess flow event or a false trigger. If a genuine leak or damage is found, repair it before restarting the system. For false activations, adjust the valve setting or address the underlying system conditions that triggered the closure. Finally, follow safety protocols when restarting the system, ensuring all checks are completed before resuming gas flow.
When to Call the Professionals
While some EFV issues can be resolved in-house, others demand professional expertise. Significant valve damage, persistent leaks, or recurring false activations warrant contacting a qualified gas engineer. Don't hesitate to seek professional help for complex issues or if you're unsure about any aspect of EFV troubleshooting.
Preventing Common EFV Problems: Proactive Measures
Preventing problems is always more effective than reacting to them. Proper system design, correct valve selection, and routine maintenance are crucial for minimizing EFV issues. Make sure the valve is appropriately sized for the application and installed according to industry best practices.
Regular inspections and maintenance can identify potential problems before they escalate. This proactive approach enhances system reliability and safety, reducing the risk of costly incidents and ensuring the long-term performance of your EFVs.
For all your solenoid valve requirements, including brass and stainless steel models, WRAS-approved drinking water systems, and ATEX-certified valves for gas applications, visit Solenoid Valve World. We offer an extensive range of high-quality valves, pneumatic components, and pressure control equipment, supported by expert technical assistance and free next-day UK delivery.
