Pneumatic System Basics: Your Complete UK Industry Guide
Understanding What Makes Pneumatic Systems Tick
Pneumatic systems play a vital role in UK manufacturing, powering a wide range of operations. They use compressed air to create mechanical motion, driving everything from automated packaging to robotic assembly. This reliance on compressed air sets pneumatic systems apart from hydraulic and electric systems. Instead of oil or electricity, these systems use a readily available and relatively safe medium.
The Principles Behind Pneumatic Power
The fundamental principle behind any pneumatic system is the controlled release of pressurized air. Imagine squeezing a balloon: the compressed air inside wants out, and its release can be used to perform work. This work can involve pushing a piston or controlling a valve. Learn more: How to master the basics of pneumatics.
This principle is further refined by manipulating pressure differentials and flow control. Just like squeezing a balloon harder generates more force, higher air pressure in a pneumatic system results in more powerful movement. Regulating airflow allows for precise control over speed and the smoothness of operations.
The Advantages of Compressed Air
For UK manufacturers, the practical benefits of using compressed air are substantial. Air is readily available and doesn't carry the same environmental risks as hydraulic fluids. Pneumatic systems also tend to be simpler and more cost-effective to maintain than electrical systems. This results in less downtime and lower operating costs, a significant advantage in a competitive market. System security is crucial, including online security. For a helpful guide, check out this website security checklist.
Furthermore, pneumatic systems offer a high degree of safety. Compressed air isn't flammable and operates at relatively low temperatures, minimizing the risk of fire or overheating. This is especially important in hazardous environments or industries with strict safety rules. This inherent safety, along with reliability and cost-effectiveness, makes pneumatic systems essential to British manufacturing.
Essential Components That Actually Matter
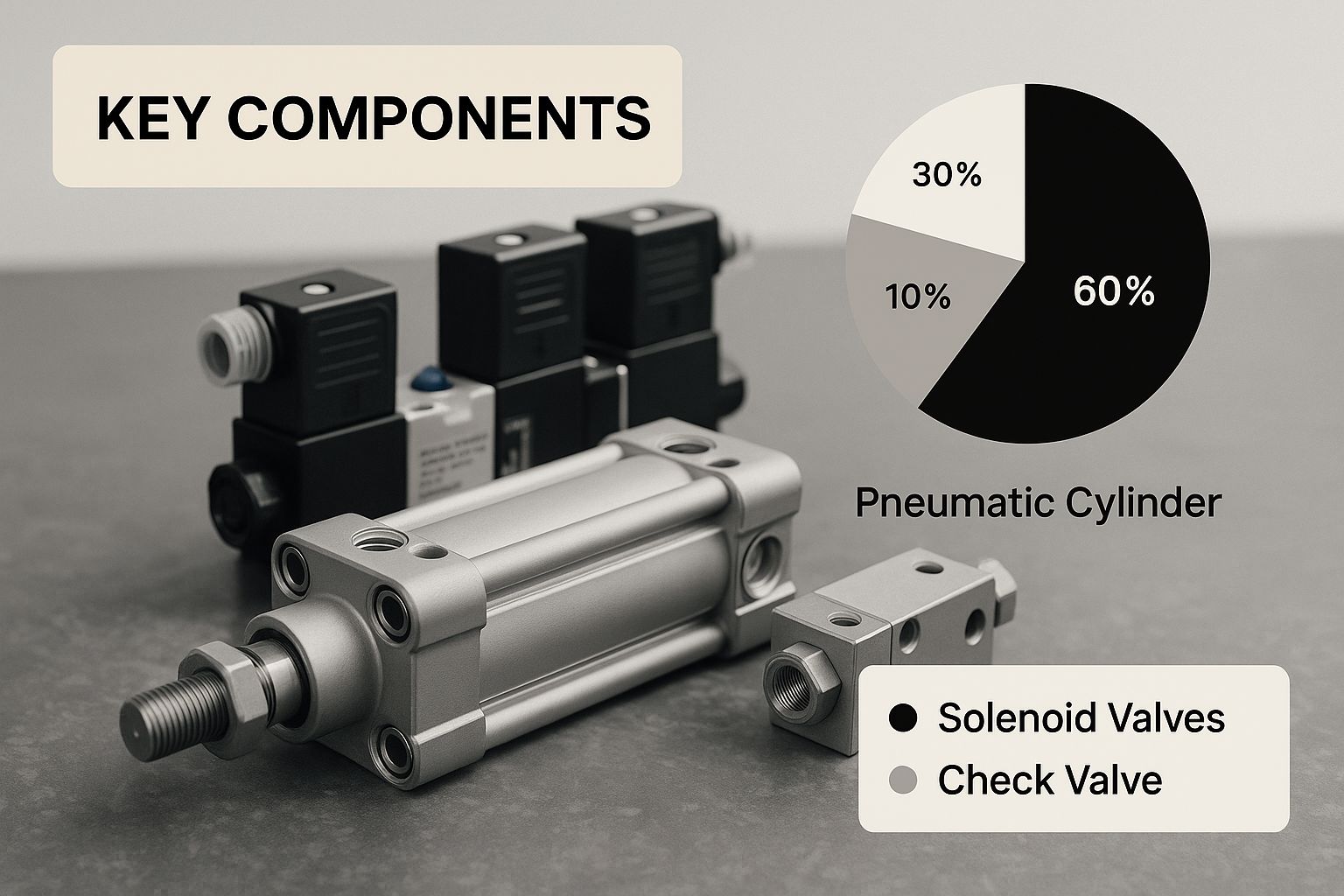
The infographic above offers a detailed look at a pneumatic cylinder and valves, highlighting the key parts of a standard pneumatic system. These components, while seemingly simple, form the foundation of powerful and adaptable systems. Understanding their individual functions is essential for effective system construction and upkeep.
Selecting the right components significantly impacts system performance, reliability, and lifespan. This goes beyond marketing claims and involves a true understanding of operational needs. For instance, choosing a high-quality compressor is crucial, as it drives the entire pneumatic system.
Compressors: The Heart of the System
Compressors generate the pressurized air that powers the entire system. The best compressor for your needs depends on factors like required pressure, airflow rate, and the specific application. Rotary screw compressors are common in UK industrial settings due to their high output and continuous operation. Reciprocating compressors are often preferred for smaller applications requiring less horsepower.
Careful consideration of your specific requirements is crucial for optimal performance.
Actuators: Turning Air Pressure into Motion
Actuators are the workhorses of pneumatic systems, converting compressed air energy into mechanical motion. They come in various designs, including linear actuators (cylinders) for straight-line movement and rotary actuators for turning or twisting motions.
Selecting the correct actuator type is fundamental for achieving the desired motion profile.
Valves: Controlling Airflow and Direction
Valves regulate airflow direction and pressure. Different valve types serve specific functions. Directional control valves manage the path of airflow, while flow control valves adjust the speed of actuators. Choosing the correct valve ensures precise and efficient system operation. For further information, explore this helpful resource: How to master Filters, Regulators, and Lubricators.
Control Components: Automation and Precision
Modern pneumatic systems often utilize electronic control components for advanced automation and precise control. Components like programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and sensors enable complex operation sequences and automated adjustments based on real-time feedback.
Investing in dependable control components guarantees a responsive and flexible system. The UK's pneumatic equipment industry is thriving, with over 150 major companies leading innovation and digital integration. These companies significantly contribute to the UK's manufacturing output, serving diverse sectors. Learn more about industry trends here: Discover more insights about UK pneumatic equipment market trends.
To further illustrate the core components of a pneumatic system and their respective roles, the following table provides a detailed comparison:
Pneumatic System Components Comparison: A detailed comparison of essential pneumatic components, their functions, typical applications, and maintenance requirements.
| Component | Primary Function | Common Applications | Maintenance Frequency | Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compressor | Generates compressed air | Powering pneumatic tools, machinery, and automation systems | Regular oil changes, filter replacements, and inspections (typically every 6 months or as per manufacturer guidelines) | 10-15 years with proper maintenance |
| Linear Actuator (Cylinder) | Converts air pressure into linear motion | Material handling, clamping, and positioning applications | Regular lubrication and seal checks (typically every 3 months or as per usage) | 5-10 years depending on the application and operating conditions |
| Rotary Actuator | Converts air pressure into rotary motion | Valve control, robotics, and conveyor systems | Regular lubrication and bearing checks (typically every 6 months or as per usage) | 5-10 years depending on the application and operating conditions |
| Directional Control Valve | Controls the direction of airflow | Directing air to different actuators or parts of the system | Periodic cleaning and inspection for leaks or wear (typically annually or as needed) | 10-15 years with proper maintenance |
| Flow Control Valve | Regulates the speed of airflow | Controlling the speed of pneumatic actuators or processes | Periodic cleaning and calibration checks (typically annually or as needed) | 10-15 years with proper maintenance |
This table summarizes the key components, their functions, applications, and typical maintenance needs. Proper maintenance is critical for maximizing component lifespan and ensuring reliable system performance.
Why UK Manufacturers Choose Pneumatic Solutions

UK manufacturers constantly strive for improved efficiency, reduced costs, and high safety standards. Pneumatic systems offer a strong solution to these needs, delivering a reliable and cost-effective power source for various applications. Many successful British businesses already benefit from this technology. This section explores why pneumatic system basics are so widely used in the UK.
Cost-Effectiveness Beyond the Initial Investment
The initial outlay for a pneumatic system is often less than hydraulic or electric options. But the financial advantages go much further. Pneumatic components typically require less maintenance, resulting in decreased downtime and lower long-term operating expenses. This directly improves profitability and strengthens the bottom line.
For instance, pneumatic actuators have a simpler design than their electric counterparts. Fewer moving parts mean less wear and tear, reducing the frequency of replacements and repairs. This inherent simplicity also simplifies troubleshooting, enabling maintenance teams to quickly identify and fix problems.
Enhanced Safety in the Workplace
Workplace safety is paramount, and pneumatic systems offer clear benefits. Compressed air is inherently safer than electricity, especially around moisture or flammable materials. This lowers the risks of electrical shocks, fires, and other dangers, creating a safer working environment.
The lower operating temperatures of pneumatic components also minimize burn and overheating risks. This is especially important in highly regulated industries where workplace safety is a top priority.
Operational Flexibility and Adaptability
Modern pneumatic systems are highly flexible, enabling manufacturers to easily adjust to changing production requirements. This adaptability is essential in today's manufacturing environment, where production lines frequently require reconfiguration for new products or processes. The modularity of pneumatic components simplifies system modifications and expansions, allowing quick and efficient changes without major re-engineering.
The strong growth of the UK pneumatics market reflects the high demand for efficient and adaptable solutions. The UK has a substantial presence in the pneumatic equipment industry, boasting a market worth millions of US dollars. Projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.3%, the market shows a strong commitment to automation and industrial efficiency. Learn more: Find more detailed statistics here.
Matching the Right Solution to the Application
While pneumatic systems offer many advantages, they are not a universal solution. Some applications requiring extremely high force or precise positioning may be better suited to hydraulic or electric systems. However, for the majority of UK manufacturing operations, pneumatic solutions offer an ideal balance of performance, cost-effectiveness, and safety. Understanding the strengths of pneumatic systems, and where other technologies might be more appropriate, is crucial for informed automation decisions.
By carefully assessing your specific needs and considering the advantages outlined above, you can determine if pneumatic system basics are the right choice for your UK manufacturing facility.
Real Applications Across UK Manufacturing

From automated assembly lines to complex processing systems, pneumatic systems power a wide range of operations within UK manufacturing. A good understanding of pneumatic system basics is essential to unlock the full potential of this adaptable technology. This section explores how different sectors use pneumatic automation to address challenges and improve performance.
Automotive: Precision and Speed on the Assembly Line
In the automotive sector, precision and speed are paramount. Pneumatic systems play a key role in achieving these objectives. Robotic arms fitted with pneumatic grippers and actuators handle intricate assembly tasks, from positioning engine components to performing precise welding operations.
This automation enhances precision, reduces errors, and speeds up production, ultimately leading to greater efficiency. Pneumatic systems also power key processes like painting and finishing. Automated spray systems, controlled by pneumatic valves, ensure consistent, high-quality finishes for every vehicle.
Food Processing: Hygiene and Reliability
Hygiene and reliability are essential in food processing. Pneumatic systems, which utilize compressed air instead of potentially contaminating hydraulic fluids, provide a clean and dependable solution for various operations.
Pneumatic conveying systems, for example, efficiently transport ingredients and finished products through pipelines, minimizing cross-contamination risks. Pneumatic controls also operate filling and packaging machinery, ensuring consistent product quality and precise portion control.
Pharmaceuticals: Maintaining Sterile Environments
The pharmaceutical industry demands strict sterility and unwavering reliability. Pneumatic systems meet these stringent requirements by offering a non-contact, clean power source.
Inside clean rooms, pneumatic actuators handle tasks like manipulating vials, operating mixing equipment, and controlling valves. This approach eliminates the risk of contamination from lubricants or electrical sparks, safeguarding product integrity and patient safety. Pneumatic systems are vital to UK pharmaceutical factories, making up approximately 25% of all mechanical automation components.
This sector continues to grow, outpacing hydraulic and electric alternatives in cost-conscious and safety-critical settings. For a deeper dive into this growth, Explore this topic further.
Packaging: Efficiency and Adaptability
In the fast-paced world of packaging, speed and flexibility are critical. Pneumatic solutions are essential for modern packaging operations. From sealing packages to controlling labeling systems, pneumatic components contribute to streamlined and efficient processes.
The ability to easily reconfigure pneumatic systems allows for seamless handling of various product sizes and packaging types. This adaptability is invaluable in meeting the ever-changing demands of consumer goods packaging.
Other Applications Across Various Industries
Beyond these core sectors, pneumatic systems offer valuable solutions across a range of industries. These include:
- Printing: Operating presses and controlling paper feed mechanisms
- Textiles: Powering looms and automating fabric handling
- Construction: Driving pneumatic tools and operating machinery
The widespread adoption of pneumatic systems underscores their versatility and adaptability across diverse industrial applications. This adaptability is rooted in the fundamental simplicity and robustness of pneumatic principles, enabling reliable performance in challenging environments.
Planning Your First Pneumatic Implementation
Moving from basic pneumatic system knowledge to a real-world setup requires careful planning. This section offers a guide for integrating pneumatic automation into your UK facility. We'll cover key decisions, from calculating air needs to choosing and installing components.
Assessing Your Needs and Defining Objectives
Before getting into technical specifics, define your automation aims. What processes do you want to enhance? What are your key performance indicators (KPIs)? These might include increased production speed, fewer errors, or better safety. Clearly defining these objectives will inform your component choices and overall system design. Pneumatic systems have practical uses in trade businesses, boosting efficiency and productivity. For a deeper dive, check out this helpful resource: Business Process Automation For Trade Businesses.
Calculating Air Requirements: Sizing Your System
Knowing your air consumption is essential for selecting the appropriate compressor. Underestimating your needs can result in low pressure and system failure, while overestimating leads to wasted energy. Consider factors such as the number of pneumatic devices, their operating pressure, and whether they’ll be running simultaneously. Online calculators or consultations with pneumatic suppliers can help you accurately determine your facility's air demand.
Don't forget to account for future expansion. Incorporating extra capacity now can prevent costly upgrades down the line.
Component Selection: Balancing Performance and Budget
Selecting the correct components is vital for long-term system reliability and efficiency. While budget is always a consideration, prioritize quality, especially for essential components like the compressor and valves. Less expensive components can lead to early failures and higher maintenance costs. Investing in robust, dependable components upfront often saves money in the long run. The UK air compressor market, essential for pneumatic systems, is expected to see substantial growth. In 2024, an estimated 65% of medium to large UK factories used air compressors, with even higher usage in sectors like automotive assembly and food packaging. Learn more about UK air compressor market trends.
UK Compliance and Safety Regulations
Your pneumatic system design and installation must comply with all relevant UK regulations. This includes adhering to pressure vessel regulations and incorporating appropriate safety precautions. Consulting a qualified engineer or a reputable pneumatic supplier ensures your system meets all required standards. This proactive approach protects your workforce and avoids potential legal complications.
Installation and Testing: Ensuring Smooth Operation
Proper installation is crucial for optimal system function. Adhere to manufacturer guidelines and best practices for connecting components and routing air lines. After installation, test the system thoroughly to detect and address any leaks or operational problems. This approach minimizes downtime and guarantees the system performs as expected from the start.
Planning for ongoing maintenance is equally important. A regular maintenance schedule, including filter changes and lubrication, will keep your system running smoothly and prevent expensive breakdowns.
Working with Suppliers: Building Long-Term Partnerships
Developing strong relationships with reputable pneumatic suppliers is highly beneficial. A reliable supplier can offer technical expertise, assist with component choices, and provide ongoing support. They can also help with troubleshooting and provide spare parts quickly, minimizing downtime. Choose a supplier with a proven track record in the UK market and experience with similar applications.
To help you understand the requirements for different pneumatic system setups, the following table outlines essential specifications.
Pneumatic System Setup Requirements
Essential requirements and specifications for different pneumatic system applications, including pressure ranges, flow rates, and component specifications.
| Application Type | Operating Pressure | Flow Rate | Key Components | Typical Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging Automation | 60-80 psi | 20-50 scfm | Cylinders, Valves, Tubing | £2,000 - £5,000 |
| Material Handling | 80-100 psi | 50-100 scfm | Air Motors, Valves, FRL Units | £5,000 - £10,000 |
| Machine Tool Operation | 100-120 psi | 100-200 scfm | Cylinders, Valves, Sensors | £10,000 - £20,000 |
This table provides a general overview. Specific requirements can vary significantly depending on the complexity and scale of the application.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure a successful first pneumatic implementation, paving the way for improved efficiency, productivity, and safety in your UK operations.
Keeping Your Systems Running Smoothly
The longevity and reliability of your pneumatic system depend heavily on proper maintenance. A well-maintained system can operate seamlessly for years, potentially saving you significant costs down the line. This section explores proven maintenance strategies used by UK facilities to ensure their pneumatic systems consistently deliver reliable performance.
Early Detection: Preventing Costly Breakdowns
Catching potential issues early is vital for preventing major breakdowns and costly repairs. Listen for unusual noises like hissing or knocking, which could indicate air leaks or worn components. Regularly inspect air lines for visible signs of damage or wear. Addressing these seemingly small problems promptly can prevent them from escalating. For more in-depth information on a critical component, check out this resource: How to master Pressure Relief Valves.
Furthermore, monitor your system's overall performance. A drop in pressure or a decrease in actuator speed can be early warning signs of a developing problem. By addressing these indicators proactively, you can avoid unexpected downtime and maintain consistent output.
Diagnostics: Pinpointing the Root Cause
When problems inevitably occur, effective diagnostic techniques are essential. Start by systematically checking each component, beginning with the compressor and progressing through the entire system. Check for leaks, blockages, and worn parts. Pressure gauges can be instrumental in pinpointing pressure drops, helping you isolate the problem area.
For example, if a cylinder is operating slowly, the issue might stem from a faulty flow control valve, a blockage in the air line, or a problem with the cylinder itself. By isolating and testing each component methodically, you can quickly identify the root cause and implement the correct solution. This targeted approach minimizes downtime and keeps repair costs manageable.
Maintenance Schedules: Maximizing Component Life
Creating a preventative maintenance schedule is key to maximizing the lifespan of your pneumatic components. This schedule should encompass regular tasks such as:
- Draining moisture from air tanks and filters
- Checking and lubricating moving parts
- Inspecting air lines for leaks and damage
- Replacing filters according to manufacturer guidelines
The frequency of these tasks will depend on the specific components in your system and the operating conditions. However, a well-defined schedule ensures that all components receive the attention they need, preventing premature wear and extending their operational life. Pneumatic solutions are renowned for their low maintenance and durability. UK data indicates pneumatic components require 50% less maintenance than their hydraulic counterparts and last 20-30% longer under comparable conditions. This inherent durability fuels industry growth, with year-on-year investment increases of 6-8% since 2020. For a deeper dive into these statistics, see the full research: Find more detailed statistics here.
Spare Parts Management and Cost-Effective Practices
Maintaining an inventory of essential spare parts is crucial for minimizing downtime. Having common replacement parts readily available allows for swift repairs, preventing extended delays waiting for parts to arrive.
Also, consider implementing cost-effective maintenance practices. Regularly cleaning and lubricating components, for example, can significantly extend their lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Choosing high-quality, durable components upfront might entail a higher initial investment but often leads to lower long-term maintenance expenses.
Performance Monitoring: Preventing Surprises
Continuous performance monitoring is a key aspect of proactive maintenance. Installing pressure sensors and flow meters at critical points within your system allows you to track performance data. This data can reveal trends and potential problems before they escalate into noticeable issues. Modern systems often integrate software that analyzes this data and provides alerts, enabling proactive maintenance and preventing unexpected downtime.
Investing in quality components, establishing a robust maintenance schedule, and embracing proactive diagnostics are essential for maximizing the lifespan and reliability of your pneumatic systems. These practices ensure your operations run smoothly and efficiently, ultimately contributing to increased productivity and profitability.
Ready to explore a wide range of high-quality pneumatic components and accessories? Visit Solenoid Valve World for all your pneumatic system needs. We offer a comprehensive selection of valves, fittings, and more, backed by expert technical support and fast UK delivery.
