Top Air Fitting Types: Find the Best for Your Pneumatic System
Decoding Air Fittings: A Quick Overview
This guide provides a concise overview of 7 common air fitting types essential for any pneumatic system. Learn to identify push-to-connect, compression, barbed, quick-disconnect, threaded (NPT/BSPT), flare, and camlock fittings. Choosing the correct air fitting type ensures leak-free and efficient operation, whether for an industrial air compressor or a smaller application. This knowledge is crucial for selecting the right components for your projects.
1. Push-to-Connect (Push-In) Fittings
Push-to-connect fittings, also known as push-in fittings, are a leading choice among air fitting types for their speed and simplicity. Designed for tool-free installation, they offer a compelling alternative to traditional fittings, especially in applications where time is of the essence. This ease of use makes them incredibly popular across various sectors in the UK, from industrial automation and instrumentation to HVAC and even municipal water treatment. But what makes them so effective, and where do they truly shine?
The core of a push-to-connect fitting lies in its internal collet mechanism. This ingenious design allows you to simply push the tubing directly into the fitting. The collet, a cleverly designed split ring within the fitting body, grips the tubing firmly, creating a tight seal. This seal is further reinforced by integrated O-rings, ensuring leak-free operation. This mechanism eliminates the need for wrenches or other tools, dramatically reducing installation time and effort, which translates to significant labour cost savings, a critical factor for any UK business.
These fittings are remarkably versatile, accommodating various thread types commonly used in the UK, including NPT, BSPT, and metric. This broad compatibility simplifies integration into existing systems and equipment. Furthermore, they can handle a respectable operating pressure range, typically between 0-150 PSI, making them suitable for a wide range of pneumatic applications. For example, in a typical factory automation setting, push-to-connect fittings can be used for connecting air lines to pneumatic cylinders, valves, and other actuators. In HVAC systems, they can be employed for connecting air lines to pressure gauges, thermostats, and other control devices. Even in the water treatment sector, specific variants of push-to-connect fittings find application in lower-pressure lines.
One of the key advantages of push-to-connect fittings is their speed of installation. Compared to traditional compression fittings, which require tightening with wrenches, push-to-connect fittings can be installed in seconds. This speed boost is invaluable in large-scale installations or situations where downtime needs to be minimized. Imagine a production line needing a quick reconfiguration; push-to-connect fittings can significantly reduce the time required for such modifications. Learn more about Push-to-Connect (Push-In) Fittings for further insights into their functionality.
Proper tube preparation is critical for a reliable seal. The tubing needs to be cut squarely and cleanly, ensuring a smooth surface for the collet to grip. Any burrs or imperfections on the tubing's end can compromise the seal and lead to leaks. While the tool-free nature of these fittings is a major advantage, investing in a good quality tube cutter is essential for consistent performance.
While push-to-connect fittings offer significant benefits, it's important to be aware of their limitations. They are generally more expensive than traditional compression fittings. This higher upfront cost, however, can be offset by the reduced labour costs associated with installation. Another factor to consider is their suitability for high-pressure applications. While suitable for many common pneumatic systems, they may not be the best choice for systems operating at extremely high pressures. In such cases, more robust fitting types might be necessary. Furthermore, while disconnection is relatively easy, it's crucial to follow the manufacturer's instructions to avoid damaging the fitting or the tubing.
For example, Parker, a leading manufacturer of pneumatic components, offers a wide range of push-to-connect fittings suitable for various applications. You can explore their offerings on their website: https://www.parker.com/us/en/products/pneumatic-fittings. Pricing will vary depending on the specific size and material of the fitting.
Push-to-connect fittings deserve their place in this list of air fitting types due to their unparalleled speed of installation, reliable sealing, and overall ease of use. They are a valuable asset for any professional dealing with pneumatic or low-pressure fluid systems, particularly in time-sensitive applications. While they may not be the perfect solution for every scenario, their benefits often outweigh their limitations, making them a go-to choice for numerous applications across various industries in the UK.
2. Compression Fittings
Compression fittings are a stalwart in the world of pneumatic and fluid systems, offering a robust and reliable connection method for various applications. As a traditional air fitting type, they secure tubing by compressing a ferrule (also known as a sleeve or olive) against the tubing's outer diameter, creating a tight mechanical seal. This method provides exceptional holding power, making compression fittings a popular choice for permanent installations and high-pressure systems commonly found in industrial settings across the UK. From heavy-duty machinery to delicate instrumentation, these fittings prove their worth across a broad spectrum of applications.
One of the key advantages of compression fittings is their cost-effectiveness, especially when compared to alternatives like push-to-connect fittings. While the initial purchase price might be similar, the long-term cost savings become apparent through their reusability. With careful disassembly and occasional ferrule replacement, these fittings can serve for extended periods, reducing the need for frequent replacements and contributing to lower maintenance costs. This characteristic makes them particularly attractive for installations where longevity and budget are key considerations.
A significant feature of compression fittings is their impressive holding strength, capable of withstanding pressures exceeding 300 PSI. This robustness makes them suitable for demanding applications where other air fitting types might fall short. Their resilience to high pressures and vibrations ensures a secure connection, minimizing the risk of leaks and system failures. This is crucial in industrial pneumatics and hydraulic systems, where maintaining consistent pressure is paramount for operational efficiency and safety. Industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and oil & gas often rely on compression fittings for their reliability in these demanding environments.
Compression fittings exhibit excellent compatibility with a variety of tubing materials, including copper, nylon, polyurethane, and polyethylene. This versatility allows engineers and technicians to select the most appropriate tubing material for their specific application, considering factors such as chemical compatibility, temperature resistance, and flexibility. This flexibility in material choice makes compression fittings adaptable to diverse operational requirements. For instance, copper tubing might be preferred for its strength and heat resistance in a high-temperature application, while nylon tubing could be chosen for its flexibility in a pneumatic control system.
While compression fittings offer numerous benefits, it's important to also acknowledge their limitations. Unlike push-to-connect fittings, which require no specialized tools, compression fittings necessitate the use of wrenches for proper assembly. This adds to the installation time and complexity, potentially increasing labour costs. The process also requires a degree of skill to avoid over-tightening, which can damage the tubing and compromise the seal. Over-tightening can lead to cracks in the tubing, particularly with more brittle materials, creating potential leak points and necessitating costly repairs or replacements.
Furthermore, servicing compression fittings in confined spaces can present challenges due to the need for wrench access. In densely packed installations, accessing these fittings for maintenance or adjustments can be difficult, requiring potentially significant disassembly of surrounding components. This can lead to extended downtime and increased maintenance complexity, especially in industrial settings where accessibility is often limited.
Despite these drawbacks, the benefits of compression fittings frequently outweigh the limitations, especially in applications where reliability, high-pressure resistance, and long-term cost savings are critical. For applications demanding a robust and durable connection, compression fittings are a proven and dependable solution. If you're considering compression fittings for your next project, resources like Swagelok (https://www.swagelok.com/en/products/fittings) provide detailed technical specifications, material options, and product information to help you make informed decisions. Choosing the right fitting is crucial for the safety, reliability, and efficiency of your pneumatic or hydraulic system, and understanding the nuances of each air fitting type will ensure you make the optimal choice for your specific needs.
3. Barbed Fittings
Barbed fittings are a common and economical choice for connecting flexible tubing in low-pressure pneumatic systems. Their defining feature is the ridged, tapered barb at the end, which inserts into the tubing and creates a friction-based seal. A hose clamp or zip tie is then used to further secure the tubing to the fitting, preventing leaks and accidental disconnections. This makes them a practical solution for applications where cost-effectiveness is a primary concern and frequent disconnections aren't anticipated. Barbed fittings excel in permanent installations where the connection remains undisturbed for extended periods. This simple yet effective design makes them a staple in various industries across the UK, including manufacturing, automation, and fluid handling. Their widespread use underscores their value as a reliable and readily available component in pneumatic systems. When considering air fitting types for low-pressure applications, barbed fittings often present an ideal balance of performance, simplicity, and cost.
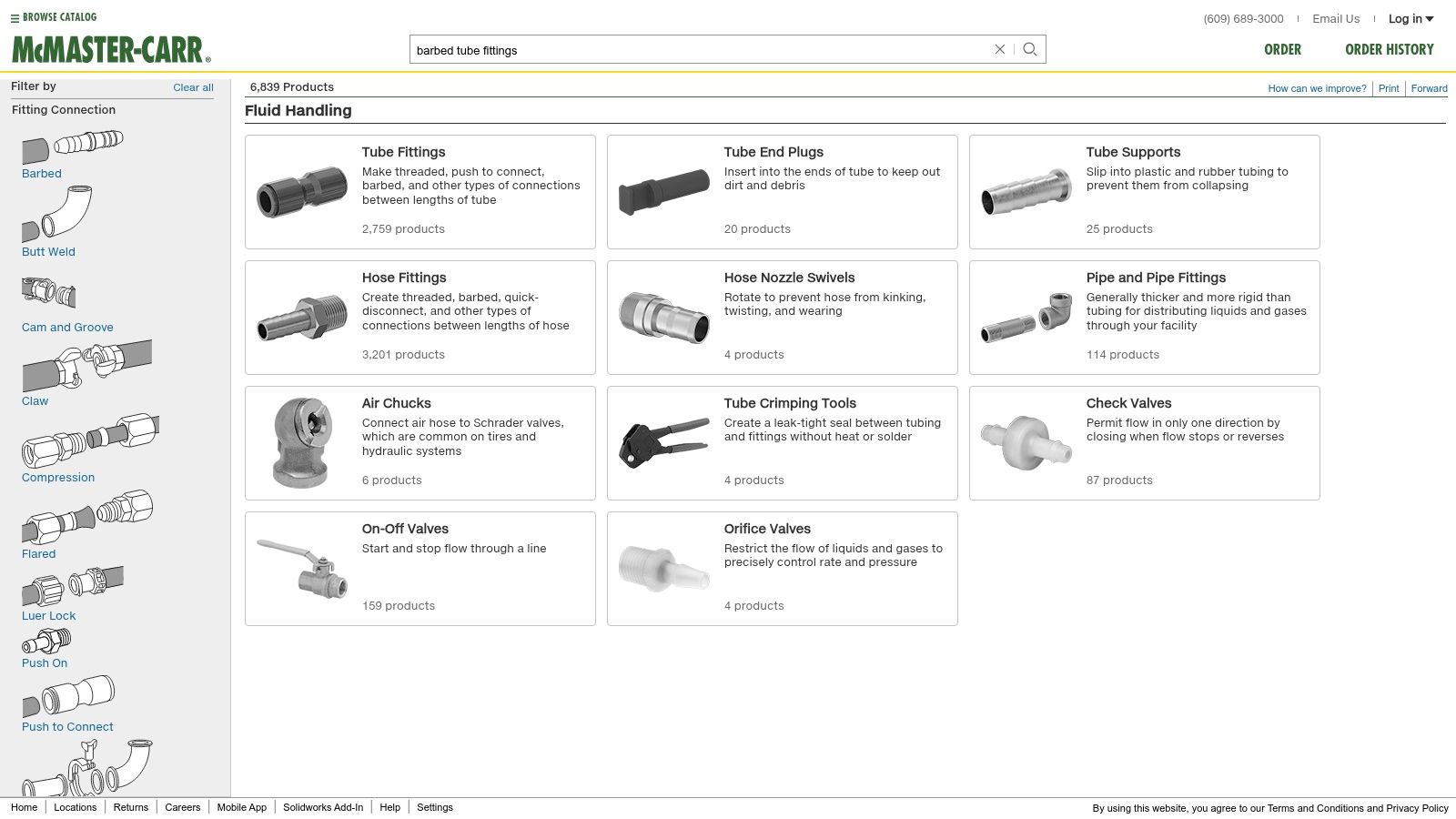
For mechanical and process engineers in the UK, barbed fittings present a straightforward solution for low-pressure air and fluid lines. They are commonly used in pneumatic control systems, robotics, and instrumentation, offering reliable performance without the complexity of more sophisticated fittings. Industrial maintenance and operations managers appreciate their ease of installation and low maintenance requirements, minimizing downtime and repair costs. HVAC and plumbing installers often utilize barbed fittings for connecting flexible tubing in drainage systems and low-pressure water lines. Municipal water treatment specialists might use them for specific applications involving low-pressure air or water distribution within treatment plants. Gas appliance and burner manufacturers sometimes employ barbed fittings for connecting low-pressure gas supply lines, although specific regulations should always be adhered to.
Barbed fittings are typically manufactured from plastic, brass, or stainless steel. Plastic fittings are the most economical and are suitable for applications with low pressure and compatible fluids. Brass fittings offer greater durability and can withstand higher pressures compared to plastic. Stainless steel fittings are the most robust and corrosion-resistant, making them suitable for harsher environments and chemically aggressive fluids. The choice of material depends on the specific application requirements, including pressure, temperature, and fluid compatibility. Pricing varies depending on the material, size, and configuration, with plastic fittings generally being the least expensive and stainless steel the most expensive. Suppliers like McMaster-Carr (linked below) provide a wide range of barbed fittings and offer detailed specifications and pricing information.
While generally reliable, barbed fittings do have some limitations. Their primary drawback is their restriction to low-pressure applications, typically below 50 PSI. Higher pressures can cause the tubing to slip off the barb, resulting in leaks. The reliance on hose clamps or zip ties introduces an extra step in the installation process and can be time-consuming, particularly when dealing with multiple connections. Disconnecting barbed fittings can be challenging and often requires cutting the tubing, making them less suitable for applications requiring frequent disconnections. Furthermore, they are incompatible with rigid tubing and are specifically designed for use with soft, flexible tubing materials like polyurethane, silicone, or PVC.
When implementing barbed fittings, it's crucial to select the correct barb size for the tubing's inner diameter. A snug fit is essential for a secure connection. Ensure the hose clamp is properly tightened to prevent leaks, but avoid over-tightening, which can damage the tubing. Double-check compatibility between the fitting material, tubing material, and the fluid being conveyed to avoid chemical reactions or degradation. For applications involving vibration or movement, consider using double clamps for added security.
Compared to push-to-connect fittings, barbed fittings are generally less expensive but also less convenient to disconnect. Push-to-connect fittings offer tool-free installation and easy disconnection, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent changes. However, they are typically more expensive than barbed fittings and have pressure limitations similar to those of barbed fittings. Compression fittings provide a more secure and robust connection than barbed fittings, making them suitable for higher pressures. However, they require more complex installation procedures and are generally more expensive. Therefore, barbed fittings remain a practical and cost-effective choice for low-pressure pneumatic systems where permanent connections are preferred and cost is a major consideration.
4. Quick-Disconnect Couplings
Quick-disconnect couplings are a crucial type of air fitting for applications requiring speed, flexibility, and minimal air loss. These ingenious devices allow for the rapid connection and disconnection of pneumatic tools and equipment without the need for tools or the interruption of system pressure. Their inclusion in any list of essential air fitting types is undeniable, especially for professionals working with portable pneumatic tools and equipment in sectors such as manufacturing, automotive, and construction. Learn more about Quick-Disconnect Couplings
The fundamental design of a quick-disconnect coupling involves two key components: a plug and a socket. The plug, typically attached to the hose or tool, is inserted into the socket, which is connected to the air supply. This two-piece system facilitates a secure and airtight seal, ensuring efficient airflow. What sets quick-disconnect couplings apart is the incorporation of automatic shut-off valves within both the plug and the socket. These valves automatically close upon disconnection, preventing air leakage and maintaining system pressure. This feature is crucial for preserving energy, minimizing downtime, and ensuring a safe working environment.
One of the most significant advantages of quick-disconnect couplings is their one-hand operation capability. This allows operators to quickly switch between different pneumatic tools without having to shut down the entire system, greatly enhancing productivity. Imagine an automotive assembly line where workers need to switch between impact wrenches, air ratchets, and spray guns multiple times a day. Quick-disconnect couplings significantly reduce downtime, contributing to a more efficient workflow. Similarly, in a maintenance setting, a technician can quickly disconnect a faulty tool and connect a replacement, minimizing disruption to ongoing operations.
Quick-disconnect couplings are available in a range of pressure ratings, typically from 150 to 300 PSI, catering to various industrial applications. Choosing the correct pressure rating is vital to ensure safe and efficient operation. Connecting a coupling with a lower pressure rating than the system pressure can lead to coupling failure and potentially hazardous situations. For UK users, it's important to consider the pressure units used in the specific application and ensure compatibility with the coupling specifications.
Furthermore, these couplings come in various actuation styles, including push-pull, twist-lock, and lever-activated mechanisms. This variety allows users to select the most appropriate coupling for their specific needs, taking into account factors such as ease of use, frequency of connection/disconnection, and the working environment. For example, in a dusty or dirty environment, a twist-lock mechanism might be preferred over a push-pull mechanism to prevent accidental disconnections.
While the benefits of quick-disconnect couplings are numerous, it's also important to acknowledge their limitations. They typically have a higher initial cost compared to permanent fittings. However, the time saved through faster tool changes and reduced downtime often offsets this higher initial investment over the long run. Another consideration is their larger profile compared to standard fittings. This can be a factor in applications where space is limited. Finally, the moving parts within the coupling require occasional maintenance, such as lubrication and cleaning, to ensure continued reliable performance.
The potential for pressure drop through the coupling is another factor to consider. While minimal, this pressure drop can impact the performance of some pneumatic tools, particularly those requiring precise air pressure regulation. It’s advisable to consult the manufacturer's specifications for both the coupling and the tool to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. More information can be found on supplier websites such as Colder.
When implementing quick-disconnect couplings, choosing the right materials is crucial. Couplings are commonly made of brass, composite plastics, or stainless steel. Brass offers a good balance of durability and cost-effectiveness, while stainless steel is preferred for corrosive environments. Composite plastics offer a lightweight and corrosion-resistant option but may have lower pressure ratings. For UK applications, it is important to check if the materials are compliant with relevant British standards.
In conclusion, quick-disconnect couplings are a valuable addition to any toolkit for professionals working with pneumatic systems. Their ability to facilitate rapid tool changes, minimise downtime, and prevent air loss makes them a worthwhile investment. By understanding the different types, features, and limitations, users can select the most appropriate quick-disconnect coupling for their specific needs, maximizing efficiency and productivity in their operations.
5. Threaded Fittings (NPT/BSPT)
Threaded fittings are a cornerstone of pneumatic and fluid systems worldwide, providing a robust and reliable method for connecting various components. These fittings utilize standard pipe threads—primarily NPT (National Pipe Thread) or BSPT (British Standard Pipe Thread)—to create secure, leak-proof seals. Reliance on thread engagement, combined with the use of sealant or tape, ensures a strong connection capable of withstanding high pressures. In the UK, BSPT is the more common standard, though NPT fittings are also encountered, particularly in equipment originating from the United States. This widespread adoption makes threaded fittings a crucial element in countless industrial applications, from simple compressed air lines to complex hydraulic systems. Threaded fittings earn their place on this list due to their strength, compatibility, and pressure handling capabilities. They offer a versatile and dependable solution for permanent connections in a wide range of pneumatic and fluid power applications.

Threaded fittings are characterized by their standardized thread profiles (NPT or BSPT), which ensure compatibility with corresponding male threads on pipes, valves, and other components. The use of a thread sealant, such as PTFE tape or a liquid sealant, is crucial for achieving a leak-free seal. These fittings are available in various materials, including brass, stainless steel, and plastic, catering to different application requirements. Common configurations include elbows, tees, couplings, reducers, and adaptors, offering flexibility in system design. Pressure ratings for threaded fittings can exceed 1000 PSI, depending on the size and material of the fitting. For precise details on thread dimensions and standards, particularly concerning differences between BSP and NPT, learn more about Threaded Fittings (NPT/BSPT).
For engineers and technicians working with pneumatic systems, understanding the nuances of threaded fittings is essential. For instance, BSPT threads have a slightly different angle and pitch compared to NPT, requiring careful selection to avoid cross-threading. In the UK, adhering to the BSPT standard is paramount for ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure and equipment. While precise pricing varies based on size, material, and configuration, threaded fittings are generally a cost-effective solution. However, the installation process can be more time-consuming compared to push-to-connect fittings, requiring careful threading and the application of sealant.
Implementing Threaded Fittings:
- Clean the threads: Ensure both male and female threads are clean and free from debris.
- Apply sealant: For BSPT fittings, wrap PTFE tape around the male threads in a clockwise direction, ensuring complete coverage. For NPT, the direction can be clockwise or anti-clockwise, but consistency is key. Liquid sealant can also be used.
- Engage the threads: Carefully thread the fitting onto the pipe or component, avoiding cross-threading.
- Tighten: Use an appropriate wrench to tighten the fitting to the specified torque. Overtightening can damage the threads or the fitting itself.
- Inspect for leaks: After pressurizing the system, inspect the connection for leaks. If a leak is detected, carefully tighten the fitting further or disassemble and reapply sealant.
Advantages of Threaded Fittings:
- Industry-standard compatibility: Adherence to NPT or BSPT standards ensures compatibility with a vast range of pneumatic components.
- High-pressure capability: Threaded fittings can handle high pressures, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications.
- Robust and durable connections: The threaded connection provides a strong and reliable seal, resistant to vibration and mechanical stress.
- Wide range of configurations: Elbows, tees, couplings, and other configurations provide flexibility in system design.
Disadvantages of Threaded Fittings:
- Requires sealant: The use of thread sealant is essential for leak-free operation, adding an extra step to the installation process.
- Time-consuming installation: Threading and sealing can be time-consuming compared to other fitting types.
- Risk of cross-threading: Care must be taken to avoid cross-threading, which can damage the threads and compromise the seal.
- Potential for galling: Stainless steel threaded fittings are susceptible to galling, particularly during assembly. Using an anti-seize lubricant can mitigate this risk.
Threaded fittings offer a time-tested solution for creating secure and reliable connections in pneumatic and fluid power systems. Their strength, compatibility, and high-pressure capability make them an indispensable component in a wide range of industrial applications. However, the installation process requires attention to detail and proper use of sealant to prevent leaks and ensure long-term performance. For those working in the UK, understanding the prevalence of the BSPT standard is crucial for ensuring compatibility and efficient system design. Brennan Industries (https://www.brennan-inc.com/products/fittings/pipe-fittings) offers a comprehensive range of threaded fittings suitable for various industrial applications.
6. Flare Fittings
Flare fittings secure their place on this list of essential air fitting types due to their robust, leak-tight connection, especially crucial in high-pressure pneumatic and hydraulic systems. These fittings employ a metal-to-metal seal, achieved by flaring the end of the tubing at a specific angle, typically 37° or 45°, which then mates with a corresponding conical seat within the fitting body. This design makes them ideal for demanding applications where reliability and performance are paramount. Think automotive braking systems, hydraulic machinery, and industrial pneumatic control systems – anywhere leaks can have significant consequences.
A key advantage of flare fittings is their ability to withstand high pressures, often exceeding 1000 PSI. This resilience makes them a preferred choice in systems handling compressed air, hydraulic fluids, and refrigerants under significant pressure. In the UK, where industries like oil and gas, aerospace, and manufacturing demand robust fluid power systems, flare fittings play a critical role in maintaining operational efficiency and safety.
The metal-to-metal sealing mechanism eliminates the need for O-rings or gaskets, components prone to wear and tear, especially under high pressure and temperature fluctuations. This not only simplifies maintenance but also enhances the long-term reliability of the connection. Unlike compression fittings that rely on a deformable ferrule, flare fittings offer a more consistent and durable seal, less susceptible to loosening due to vibration or thermal cycling.
Features and Benefits:
- 37° or 45° flare angle options: This caters to different system requirements and international standards. 45° is more common in the UK for general hydraulic and pneumatic applications, while 37° is frequently found in automotive and refrigeration systems.
- Metal-to-metal sealing surface: Ensures a robust, leak-proof connection, even under high pressure and vibration.
- High-pressure capability (1000+ PSI): Makes them suitable for demanding hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
- Reusable with proper tube condition: Offers long-term cost savings by allowing reuse of the fittings if the tubing remains undamaged.
- Vibration resistant connection: Essential for applications where vibration could compromise the integrity of the seal, such as mobile hydraulic equipment or industrial machinery.
Implementation and Setup Tips:
Proper installation is crucial for the effective performance of flare fittings. This involves using a specialized flaring tool to create the precise flare angle on the tubing. Here's a breakdown of the process:
- Cut the tubing squarely: A clean, square cut is essential for a proper flare. Use a tube cutter designed for the specific tubing material to avoid crushing or deforming the end.
- Deburr the tubing: Remove any burrs or sharp edges from both the inside and outside of the cut end.
- Clamp the tubing: Secure the tubing in the flaring tool, ensuring the correct amount of tubing protrudes for the desired flare.
- Flare the tubing: Follow the manufacturer's instructions for operating the flaring tool. Apply even pressure to create a smooth, uniform flare.
- Inspect the flare: Check for cracks, imperfections, or unevenness in the flare. A poorly formed flare can compromise the seal and lead to leaks.
- Assemble the fitting: Carefully tighten the fitting nut onto the flared tubing, ensuring proper alignment and a snug fit. Avoid overtightening, which can damage the fitting or tubing.
Pricing and Technical Requirements:
Pricing for flare fittings varies depending on the material (brass, steel, stainless steel), size, and pressure rating. In the UK, expect to pay anywhere from a few pounds for individual brass fittings to significantly more for specialized high-pressure stainless steel fittings. Technical requirements, including pressure and temperature ratings, are typically specified by the manufacturer and should be carefully considered based on the application.
Comparison with other fitting types:
While compression fittings offer a simpler installation process, they don't match the pressure handling capabilities or vibration resistance of flare fittings. Similarly, push-to-connect fittings are quick and easy to use but are typically limited to lower pressures. For high-pressure applications where a robust and leak-proof connection is paramount, flare fittings remain the preferred choice.
Resources:
For a more in-depth look at hydraulic fittings and adapters, including flare fittings, visit Eaton. They offer a wide range of products and technical information.
In conclusion, flare fittings, despite the higher initial setup complexity, offer a superior solution for demanding high-pressure applications. Their metal-to-metal seal, vibration resistance, and reusability make them a valuable asset across various industries in the UK and beyond. By understanding their features, benefits, and proper installation techniques, engineers and technicians can ensure the reliability and efficiency of critical fluid power systems.
7. Camlock Fittings
Camlock fittings, also known as cam and groove couplings, secure their place on this list of essential air fitting types due to their remarkable ability to quickly and securely connect and disconnect large-bore pneumatic lines. This makes them invaluable for applications where speed and efficiency are paramount, such as in dust collection systems, material handling, and bulk transfer operations common in many UK industries. These fittings are especially well-suited for situations requiring frequent connections and disconnections, offering a significant advantage over more time-consuming alternatives like threaded connections.
Camlock fittings operate using a simple yet effective cam-operated lever mechanism. The fitting consists of a male adapter with grooves and a female coupler with cam arms. To connect, the male adapter is inserted into the female coupler, and the cam arms are rotated downwards. This action locks the two components together, creating a tight seal. Disconnection is just as swift, requiring only a lift and twist of the cam levers.
One of the key advantages of camlock fittings is their availability in a wide range of sizes, typically from 1" to 6" and even larger in certain specialized applications. This large bore capability makes them ideal for handling high-volume airflow in industrial settings. They are also manufactured in various materials to suit diverse operational needs and environments. Common materials include aluminium, stainless steel, brass, and polypropylene. Aluminium offers a balance of cost-effectiveness and durability, while stainless steel provides excellent corrosion resistance for harsh environments encountered in chemical processing or marine applications. Brass offers a good combination of strength and corrosion resistance and is often used in pneumatic systems. Polypropylene is a lightweight and cost-effective option suitable for less demanding applications.
The gasket sealing system within a camlock fitting is crucial for leak prevention. These gaskets, typically made of Buna-N, EPDM, or Viton, create a tight seal between the male and female components, ensuring minimal air loss and maintaining system pressure. However, it's essential to consider that these gaskets are wear items and require periodic inspection and replacement to maintain optimal performance. Over time, exposure to chemicals, temperature fluctuations, and general wear and tear can degrade the gasket material, leading to potential leaks and reduced efficiency.
While camlock fittings offer significant advantages, they also have some limitations. They are generally suited for lower pressure applications, typically under 150 PSI. For higher-pressure pneumatic systems, alternative fitting types like threaded or flanged connections might be more appropriate. Furthermore, camlock fittings tend to be larger and heavier than other fitting types, which might be a consideration in space-constrained applications. Also, although the initial cost of the fittings themselves might be comparable to other options, the periodic gasket replacement adds to the overall long-term cost, especially for smaller diameter applications where other, simpler solutions might suffice.
Compared to other quick connect fittings like push-to-connect fittings, camlock fittings offer a more secure locking mechanism for high-flow applications, though they are generally more expensive and less compact. While push-to-connect fittings excel in ease of use for smaller diameter, lower-flow applications, they might not provide the same robust and leak-free connection for the larger bore sizes typically used with camlock fittings.
When implementing camlock fittings, it's crucial to select the appropriate material and size for your specific application. Ensure compatibility with the intended air pressure and temperature, and choose gaskets that are chemically compatible with the medium being transported. Regular inspection and timely replacement of gaskets are essential for preventing leaks and maintaining system efficiency. For applications involving hazardous materials, ensure compliance with relevant safety regulations and best practices.
Pricing for camlock fittings varies depending on the size, material, and supplier. You can expect to pay anywhere from £10 for smaller, polypropylene fittings up to £100 or more for larger, stainless steel versions. A good starting point for sourcing camlock fittings in the UK would be Dixon Valve (https://www.dixonvalve.com/products/cam-and-groove-couplings), a reputable manufacturer offering a wide range of cam and groove couplings. It is always recommended to compare pricing and specifications from different suppliers to ensure the best value for your specific needs. Always consult with a qualified engineer if you have any doubts regarding the selection or installation of camlock fittings for your pneumatic system.
Air Fitting Types Comparison Summary
| Fitting Type | Core Features & Pressure ★ | User Experience & Ease ✨ | Target Audience 👥 | Unique Selling Points 🏆 | Price & Value 💰 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Push-to-Connect (Push-In) | Tool-free, O-ring seal, 0-150 PSI ★★★★☆ | Fast install/removal, no tools needed ✨ | Automation & general pneumatics 👥 | Quick install, reliable seal ✨ | Moderate cost, faster labor 💰 |
| Compression Fittings | Ferrule seal, up to 300+ PSI ★★★★★ | Requires wrenches, more complex install | Industrial pneumatics & hydraulics 👥 | High pressure, reusable fittings 🏆 | Lower cost, durable 💰 |
| Barbed Fittings | Ridged, clamp-secured, under 50 PSI ★★★☆☆ | Simple, clamp required, low tech | Low-pressure flexible tubing 👥 | Most economical, simple design ✨ | Very low cost 💰 |
| Quick-Disconnect Couplings | Plug/socket, auto shut-off, 150-300 PSI ★★★★☆ | One-hand rapid connect/disconnect ✨ | Portable tools & frequent changing 👥 | No air loss, fast tool swaps 🏆 | Higher cost, convenient 💰 |
| Threaded Fittings (NPT/BSPT) | Standard pipe threads, up to 1000+ PSI ★★★★★ | Time-consuming, requires sealant | Industrial pneumatics & plumbing 👥 | Industry standard, very durable 🏆 | Moderate cost, proven value 💰 |
| Flare Fittings | Metal-to-metal seal, 1000+ PSI ★★★★★ | Specialized tools, precise prep needed | High-pressure pneumatics, hydraulics 👥 | Leak-tight, vibration resistant 🏆 | Moderate to high 💰 |
| Camlock Fittings | Cam lever, large bore, <150 PSI ★★★☆☆ | Quick connect for large lines, heavier | Bulk transfer, material handling 👥 | Fast large line connect, corrosion resistant ✨ | Higher cost, niche use 💰 |
Choosing the Right Air Fitting: Key Considerations
From push-to-connect convenience to the robust reliability of threaded fittings, understanding the various air fitting types is crucial for any system involving pneumatics. This article explored seven common types: push-to-connect, compression, barbed, quick-disconnect, threaded (NPT/BSPT), flare, and camlock fittings. Each offers unique advantages and disadvantages depending on the application. Remember, the most important takeaways when selecting air fitting types are compatibility with your tubing material, pressure requirements, and the frequency of connection and disconnection. Managing these various types, particularly across a large property portfolio, can quickly become complex. For insights on streamlining these and other building operations, resources like this article on commercial property management from Tereo offer valuable tips for improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
When implementing your chosen air fittings, consider factors such as potential leak points, required maintenance, and the overall cost-effectiveness of the system. The right air fitting can drastically improve system performance, prevent costly downtime, and contribute to a safer working environment. By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure a reliable and efficient pneumatic system tailored to your specific needs.
For a wide selection of high-quality air fitting types and expert advice, visit Solenoid Valve World. They provide a comprehensive range of pneumatic components to help you build and maintain robust and efficient systems.
