Pneumatic Solenoid Valves: Your Complete UK Industry Guide
Understanding How Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Actually Work
Pneumatic solenoid valves play a crucial role in many UK industries, controlling the flow of compressed air in a wide range of applications, from automated assembly lines to complex robotic systems. These compact devices function as electrically controlled switches, precisely regulating airflow to power pneumatic actuators, cylinders, and other essential equipment. Understanding their operation is vital for selecting the right valve and ensuring its reliability over time.
The Heart of the Matter: Solenoid and Valve Body
At the center of a pneumatic solenoid valve is the solenoid. This electromagnetic coil generates a magnetic field when energized with electricity. This field interacts with a movable plunger or armature inside the valve body. The valve body itself contains the internal air passages and is typically constructed from durable materials like brass or stainless steel, known for their resistance to corrosion and wear.
From Electrical Signal to Mechanical Action
When an electrical signal reaches the solenoid, the generated magnetic field causes the plunger to shift position. This movement opens or closes the valve, regulating the passage of compressed air. A normally closed valve stays shut until energized, at which point the solenoid pulls the plunger open, allowing air to flow. In contrast, a normally open valve remains open until energized. Then, the solenoid pushes the plunger closed, blocking the airflow. For a deeper dive into pneumatic systems, check out Pneumatic System Basics.
Direct-Acting vs. Pilot-Operated Valves
Pneumatic solenoid valves are generally classified as either direct-acting or pilot-operated. Direct-acting valves rely solely on the solenoid's force to move the plunger. Pilot-operated valves, however, use a small amount of air pressure to assist the valve's operation. This design allows for control of larger airflow volumes with a smaller solenoid, increasing energy efficiency. To further understand these principles, exploring similar mechanisms in other fields can be helpful, such as the processes described in How Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Actually Work.
Seals and Other Crucial Components
Reliable sealing is essential for preventing leaks and maintaining efficient valve operation. Materials like Viton or PTFE are commonly used to create airtight seals between the moving parts. Other vital components include the spring, which returns the plunger to its resting position when the solenoid is de-energized, and the orifice, a precisely sized opening that regulates the valve’s flow capacity.
While precise data specifically for pneumatic solenoid valves in the UK is hard to isolate, overall market trends offer helpful insights. In 2023, the UK control valve market, which includes pneumatic solenoid valves, reached an estimated value of $292 million (according to Market Research Future). This suggests strong demand driven by the growth of automation and the UK's focus on energy efficiency. This increased adoption of automation across various British industries, from manufacturing to water treatment, highlights the growing significance of pneumatic solenoid valves in modern control systems.
What's Driving Demand Across British Industry
The UK's industrial sector is evolving, with automation and Industry 4.0 at the forefront. This shift is creating a significant increase in demand for advanced control systems. At the core of many of these systems are pneumatic solenoid valves. These valves offer precise control over pneumatic systems, making them vital for various applications across British industries.
Automotive and Pharmaceutical Sectors Embrace Precision
The automotive industry, a key component of British manufacturing, heavily relies on automated processes. Pneumatic solenoid valves are essential for controlling robotic arms, assembly line equipment, and painting systems.
The pharmaceutical sector also demands precise process control. Here, pneumatic solenoid valves are crucial for ensuring the accurate dispensing, mixing, and packaging of sensitive materials.
Packaging Operations Prioritize Speed and Efficiency
In packaging, speed and efficiency are paramount. Pneumatic solenoid valves contribute to faster cycle times and precise control over packaging machinery. This results in higher throughput and reduced waste.
This is especially important for food and beverage packaging where maintaining hygiene and preventing contamination are vital.
Market Trends: Resilience and Steady Growth
The increasing demand for pneumatic solenoid valves is reflected in market data. The UK market for hydraulic and pneumatic valves, which includes pneumatic solenoid valve technologies, has shown resilience amidst fluctuating trends.
From 2013 to 2023, the market experienced both growth and decline. Notable downturns occurred in 2016 and 2020, with declines of -9.55% and -16.97% respectively. However, a robust recovery of 21.74% followed in 2021. By 2023, the market reached a value of 605.91 million euros. A projected CAGR of 0.78% between 2024 and 2028 suggests continued, steady growth. Learn more about market trends for pneumatic valves.
Regulatory Changes and Sustainability Drive Innovation
Several factors are contributing to the increasing demand for pneumatic solenoid valves. Stringent regulatory changes, particularly those related to emissions and energy efficiency, are pushing businesses to adopt more sustainable technologies.
Pneumatic solenoid valves, with their ability to optimize air consumption and reduce energy waste, are well-suited to meet these new requirements.
Navigating Supply Chain Challenges and Cost Considerations
UK procurement teams are facing ongoing supply chain disruptions and cost pressures. However, the long-term benefits of investing in high-quality pneumatic solenoid valves, such as reduced maintenance and increased operational efficiency, often outweigh the initial investment.
This understanding is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that support both long-term sustainability and productivity.
Industry 4.0 and the Future of Automation
The transition towards Industry 4.0, marked by interconnected systems and data-driven decision-making, further fuels the demand for intelligent control systems. Pneumatic solenoid valves, with their precise control capabilities and seamless integration with sophisticated automation platforms, are vital components of this industrial evolution.
As UK industries continue to adopt automation and data-driven optimization, the importance of pneumatic solenoid valves will only grow in the years to come.
Choosing The Right Configuration For Your Application
Selecting the right pneumatic solenoid valve configuration is crucial for optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in any UK industrial setting. Making the wrong choice can lead to system inefficiencies, costly downtime, and even safety hazards. This guide helps you navigate the various valve types and configurations, ensuring you make an informed decision.
Two-Way, Three-Way, and Multi-Port Valves
The first step involves choosing the number of ports. This determines the valve's flow paths. Two-way valves, the simplest type, act like on/off switches, ideal for basic airflow control. Think of them as controlling a single tap.
Three-way valves have an additional exhaust port, allowing them to divert airflow between two paths, much like a shower diverter valve.
For more complex systems requiring multiple flow paths, multi-port valves provide the necessary versatility. For instance, a multi-port valve could manage airflow to different pneumatic actuators in a robotic arm.
Normally Open vs. Normally Closed
Next, consider the valve's default state: normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC). NO valves allow airflow until energized, while NC valves remain closed until activated.
The wrong choice can lead to safety issues. A safety interlock, for example, requires an NC valve to prevent unintended operation. For applications like ventilation, where constant airflow is usually desired, an NO valve is more suitable.
Direct-Acting vs. Pilot-Operated
Understanding the difference between direct-acting and pilot-operated valves is crucial. Direct-acting valves rely solely on the solenoid's force for actuation, making them suitable for lower pressure applications.
Pilot-operated valves use system pressure to assist operation, allowing them to control larger airflow volumes with smaller solenoids, increasing energy efficiency. In high-pressure applications, common in heavy machinery, pilot-operated valves are often the better choice.
Mounting Options, Connections, and Voltage
Practical considerations, such as mounting options, connection types, and voltage requirements, significantly impact installation costs and long-term reliability. Standard threaded connections simplify installation in existing UK pipework. Specialized flanges may be necessary for high-pressure systems. Compatibility with the UK mains voltage (230V) is essential for reliable operation. Choosing a valve with readily available replacement parts in the UK simplifies maintenance and minimizes downtime.
To help you visualize the differences between common pneumatic solenoid valve configurations, we've compiled the following comparison:
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Configuration Comparison: A comprehensive comparison of different valve types, their applications, and key specifications for UK industrial use.
| Valve Type | Typical Applications | Pressure Range | Response Time | UK Industry Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Way | Simple on/off control, basic airflow regulation | Low to Medium | Fast | Packaging, basic automation |
| 3-Way | Diverting airflow between two paths | Low to Medium | Medium | Pneumatic tools, HVAC systems |
| Multi-Port | Complex systems with multiple flow paths | Medium to High | Medium to Slow | Robotics, complex automation |
| Direct-Acting | Low-pressure applications | Low | Fast | Simple control systems |
| Pilot-Operated | High-pressure, high-flow applications | Medium to High | Medium | Heavy machinery, industrial processes |
This table provides a quick overview of the typical applications and characteristics of different valve types. Remember to consult detailed specifications when selecting a valve for your specific needs.
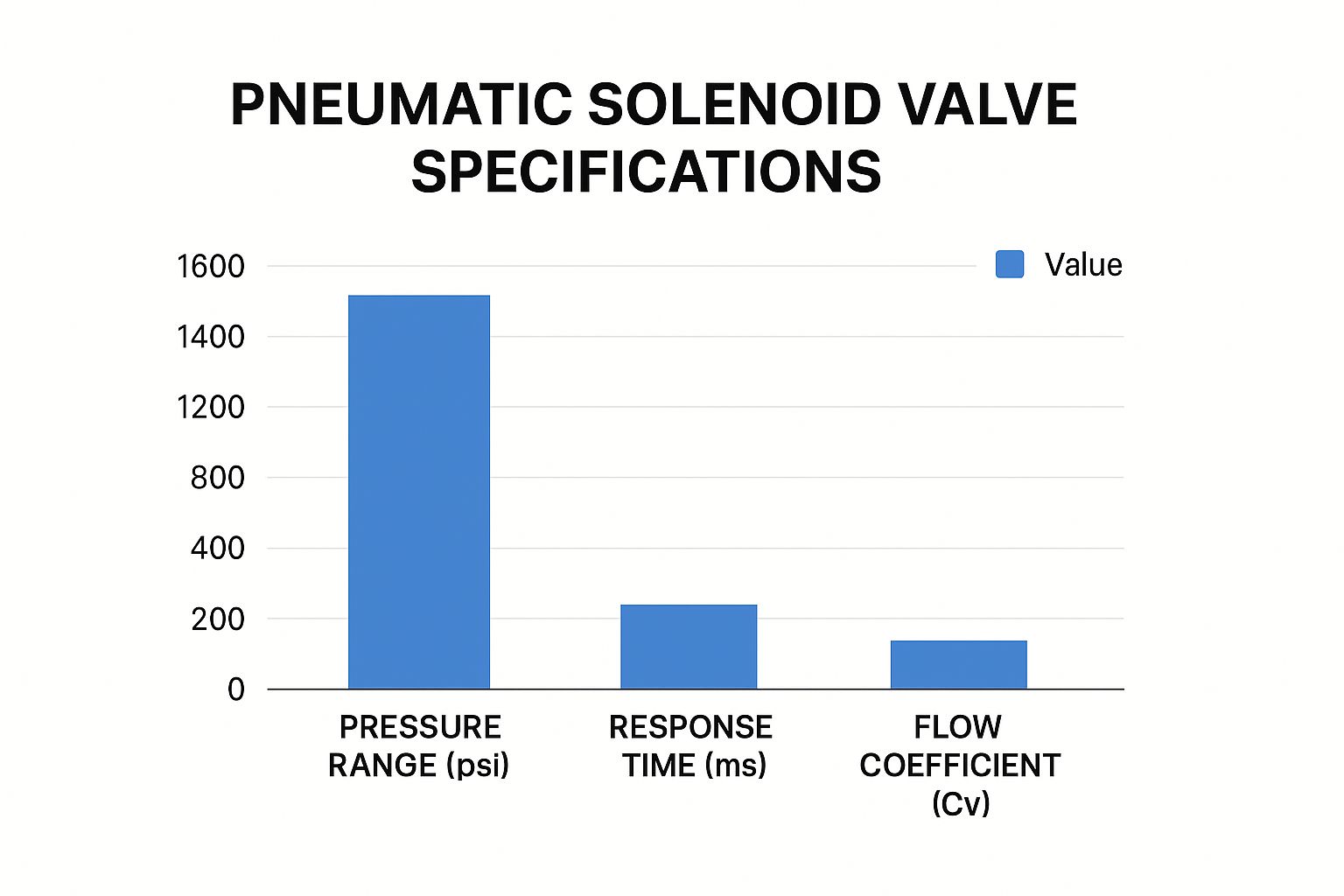
The bar chart above compares pressure range, response time, and flow coefficient – three key specifications for pneumatic solenoid valves. The data shows that some valves excel in pressure range, while others prioritize faster response times or higher flow coefficients. This trade-off highlights the need for a valve optimized for your application. For more detailed guidance, see our Selection Guide.
Smart Selection Criteria That Actually Matter

Choosing pneumatic solenoid valves based solely on price can lead to significant problems later on. Experienced engineers in the UK know that a valve's suitability hinges on several key factors. This section will give you the insights needed to make informed decisions and avoid common mistakes.
Operating Pressure and Flow Requirements
One of the most crucial factors is the operating pressure range. Pneumatic systems operate under varying pressures, and your valve must handle these specific pressures, both maximum and minimum. A valve designed for low-pressure might fail if used in a high-pressure system.
Similarly, flow requirements, measured by the flow coefficient (Cv), dictate how much air the valve can manage. An inadequate Cv can hinder system performance and create inefficiencies. Accurately calculating your application's required Cv is crucial for optimal operation. You might find this helpful: How to master valve selection.
Environmental Factors and Media Compatibility
Industrial settings in the UK vary greatly, from climate-controlled cleanrooms to harsh outdoor conditions. Temperature extremes, humidity, and vibration can significantly impact valve performance. A valve in an unheated facility, for instance, must withstand freezing temperatures without malfunctioning.
Media compatibility is also critical. The valve's internal parts, including seals and the body, must be compatible with the controlled media. This is especially important when dealing with aggressive chemicals or corrosive materials. Incorrect material selection can lead to premature failure and potential system contamination.
Electrical Requirements and UK Safety Standards
Integrating pneumatic solenoid valves with existing control systems requires careful consideration of electrical requirements. Ensure compatibility between the valve's voltage rating and power consumption and your control system. Compliance with UK safety standards is essential, especially in hazardous environments. This often means choosing valves with specific certifications.
Specification Sheets and System Integration
Carefully reviewing manufacturer-provided specification sheets is vital. These contain crucial information about operating characteristics, materials, and certifications. Understanding these details helps you match valve capabilities to system demands, including parameters like pressure drop and response time.
Finally, consider system integration practically. This involves selecting suitable connection types and mounting options while ensuring compatibility with existing pneumatic infrastructure common in UK manufacturing. Careful planning here minimizes installation issues and ensures smooth integration with your system.
Installation Strategies That Prevent Future Headaches
Proper installation is crucial for the reliable service of your pneumatic solenoid valves and prevents them from becoming maintenance nightmares. This guide focuses on practical installation practices specifically for UK industrial environments, encompassing everything from correct mounting to electrical connections compliant with British standards.
Preparing Your Pneumatic Lines and Filtration
Before installing your valves, ensure your pneumatic lines are clean and free of debris. Contaminants in the lines can damage the valve's internal components, causing premature wear and potential failures. This is particularly important in older installations where rust or other particles may have accumulated within the pipework.
Effective filtration is paramount. Installing a filter upstream of the valve safeguards it from these harmful particles. Select a filter with the appropriate micron rating for your specific application. A filter that's too fine can restrict airflow, while one that's too coarse won't effectively trap contaminants.
Air Quality: A Critical Factor
Maintaining proper air quality is essential for the long-term health of your valves. Moisture in the compressed air can cause corrosion and damage seals. An air dryer, installed upstream of the filter, removes excess moisture, prolonging the lifespan of your valves. Also, ensure the compressed air supply meets the required pressure and flow rate specifications for your chosen valve.
Mounting Orientation and Electrical Connections
The mounting orientation of the valve can affect its performance. Some valves can be mounted in any position, while others require a specific orientation for optimal operation. Refer to the manufacturer's documentation for guidance. Incorrect mounting can lead to premature wear or even complete valve failure.
Electrical connections must adhere to British standards. Use correctly sized wiring and ensure secure connections to prevent voltage drops or overheating. Incorrect wiring can damage the valve's solenoid and create a safety hazard. Always double-check your connections and consult a qualified electrician if needed.
Integration Sequencing and Avoiding Common Pitfalls
For complex automated systems, correct integration sequencing is essential. This involves installing the valves in the proper order and ensuring correct timing and synchronization with other system components. For instance, in a robotic assembly line, the timing of valve actuation must be precisely coordinated with the robot's movements.
Over-tightening connections is a common installation mistake. This can damage the valve body or connecting pipework, causing leaks. Use the correct tools and torque settings to prevent this. Another frequent error is neglecting to lubricate moving parts, leading to increased wear and friction.
Documentation and Commissioning
Thorough documentation is vital. Maintain records of wiring diagrams, connection details, and maintenance schedules. This documentation is invaluable for troubleshooting and future maintenance. Proper commissioning procedures, including testing and verifying valve operation, ensure optimal performance from the start.
Existing Infrastructure and UK Regulations
When working with existing infrastructure, assess its compatibility with the new valves. Older pipework may require upgrades or replacement to meet the necessary pressure and flow specifications. Always comply with relevant UK health and safety regulations during installation. For example, ensure appropriate lockout/tagout procedures are followed when working with pressurized air systems.
By following these installation strategies, you can ensure the long-term reliability and performance of your pneumatic solenoid valves, minimizing costly downtime and maximizing your investment. Choosing the right configuration for your needs is also crucial, so consider resources like Choosing The Right Configuration For Your Application.
Keeping Your Valves Running And Staying Compliant

Effective maintenance is crucial for the longevity and dependability of your pneumatic solenoid valves. This directly impacts downtime and costs for UK businesses. This section explores both preventive and corrective maintenance, helping you maintain efficient and compliant systems.
Preventive Maintenance: Stopping Problems Before They Start
Regular preventive maintenance is key to reliable valve operation. This proactive strategy identifies potential issues early, preventing expensive breakdowns.
A well-structured preventive maintenance plan should include:
- Regular Inspections: Inspect valves periodically for wear and tear, such as leaks, corrosion, or damage to the valve body and connections.
- Cleaning: Remove debris and build-up to keep valves clean. This is especially important in harsh or dusty environments.
- Lubrication: Lubricate moving parts like the plunger and seals as directed by the manufacturer. This minimizes friction and extends the valve's lifespan.
- Filter Maintenance: Regularly check, clean, or replace air filters. This prevents contaminants from damaging the valve.
- Air Quality Checks: Maintain a consistent supply of dry, clean compressed air. Excess moisture or contaminants can cause corrosion and premature wear.
Corrective Maintenance: Troubleshooting and Repair
Even with the best preventive maintenance, issues can still occur. This is where effective corrective maintenance is essential.
- Troubleshooting: Begin by identifying the symptom. Is the valve leaking? Is it failing to actuate? Diagnosing the root cause is crucial for finding the right solution.
- Common Issues: Common problems include clogged orifices, worn seals, or faulty solenoids. Cleaning, component replacement, or adjustments can often resolve these issues.
The following table provides a helpful guide for diagnosing and addressing common pneumatic solenoid valve problems:
Common Valve Issues and Solutions: A diagnostic table showing typical problems, symptoms, causes, and corrective actions for pneumatic solenoid valves.
| Problem | Symptoms | Likely Cause | Corrective Action | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valve Not Opening | No airflow when energized | Faulty solenoid, blockage | Replace solenoid, clear blockage | Regular inspections and cleaning |
| Valve Not Closing | Continuous airflow | Worn seal, debris | Replace seal, clean valve | Filter maintenance, air quality checks |
| Slow Response | Delayed actuation | Weak spring, low pressure | Replace spring, check air pressure | Regular lubrication, pressure checks |
| External Leaks | Visible leakage around connections | Damaged seals or threads | Replace seals, tighten or repair connections | Proper installation, regular inspections |
This table helps pinpoint the likely cause of a problem and suggests appropriate corrective actions. Regular preventive maintenance is the best way to avoid these issues altogether.
For more complex problems, consult a qualified technician or the valve manufacturer's technical support. You might find high-pressure solenoid valve resources helpful.
UK Regulations and Compliance
Compliance with UK regulations is essential. Ensure all maintenance procedures adhere to relevant health and safety standards. Maintaining thorough documentation of all maintenance activities is also critical for demonstrating compliance. Pro audio repair can sometimes be helpful for quick resolution of pneumatic solenoid valve issues.
Spare Parts and Supplier Relationships
Keeping essential spare parts like seals and solenoids on hand minimizes downtime. Strong relationships with reliable UK suppliers ensure timely access to parts and valuable technical expertise.
Replacement vs. Repair
Sometimes replacing a valve is more cost-effective than repairing it, particularly for older or extensively damaged valves. Consider the repair cost, spare part availability, and the likelihood of future failures. A cost-benefit analysis can help you make the right decision.
Key Takeaways
This section offers a practical guide to successfully using pneumatic solenoid valves in UK industrial settings. We'll cover essential insights from successful installations, highlight common pitfalls, and define key performance indicators.
Selecting the Right Valve: A Checklist
Choosing the right pneumatic solenoid valve is crucial. Use this checklist to ensure your selection aligns with your needs:
- Application: Define your application. Will the valve manage a simple on/off function or a more complex process?
- Media: Identify the media type (air, water, oil, gas, etc.). This affects material compatibility and seal choices.
- Pressure and Flow: Determine the operating pressure range and required flow rate (Cv) to ensure the valve handles your system's demands.
- Configuration: Choose the valve type (2-way, 3-way, multi-port) and actuation (normally open or normally closed).
- Environment: Consider the operating environment (temperature, humidity, and corrosive substance exposure).
- Electrical Requirements: Verify voltage compatibility and power consumption for seamless control system integration.
- UK Standards: Ensure compliance with relevant UK safety and industry regulations.
Installation Best Practices: Avoiding Future Headaches
Proper installation is essential for long-term reliability. Follow these best practices:
- Cleanliness: Ensure clean pneumatic lines, free of debris, before installation.
- Filtration and Air Quality: Install filters and air dryers to protect the valve from contaminants and moisture.
- Mounting: Follow manufacturer guidelines for correct mounting orientation.
- Electrical Connections: Adhere to UK wiring standards; ensure secure, properly sized connections.
- Testing and Commissioning: Verify correct operation and system integration after installation.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of installation procedures, wiring diagrams, and component specifications.
Maintenance Strategies: Maximizing Valve Lifespan
Effective maintenance prevents costly downtime. Implement a comprehensive maintenance plan:
- Regular Inspections: Visually inspect valves for wear, leaks, or damage.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Clean valves regularly and lubricate moving parts as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Component Replacement: Proactively replace worn seals, filters, or other components.
- Troubleshooting: Develop a systematic approach to diagnose and resolve valve issues. Refer to troubleshooting guides and resources like those addressing high-pressure solenoid valves.
- Compliance: Ensure maintenance procedures comply with all applicable UK health and safety regulations.
Realistic Expectations and Performance Metrics
Understanding realistic performance expectations and establishing measurable metrics is crucial for evaluating your valve system's effectiveness.
- Valve Lifespan: A well-maintained pneumatic solenoid valve can operate reliably for years, though lifespan varies based on application and maintenance.
- Response Time: Different valve types have varying response times. Establish acceptable benchmarks based on your application.
- Air Consumption: Monitor air consumption to identify leaks or inefficiencies. Optimizing air usage can save costs.
- Downtime: Track downtime related to valve issues to identify areas for maintenance procedure improvement.
- Supplier Performance: Evaluate supplier reliability, technical support, and spare parts availability. Strong supplier relationships are key for efficient maintenance and minimizing downtime.
By implementing these key takeaways and best practices, you can optimize the performance, reliability, and lifespan of your pneumatic solenoid valves, leading to a safer, more efficient, and cost-effective operation. Need pneumatic solenoid valves in the UK? Visit Solenoid Valve World for a wide selection of high-quality valves, components, and expert advice. We offer free next-day UK delivery and UK-based technical support.
