How vacuum is measured.
Vacuum, or the absence of matter (air, gas or fluid) in a given space, is measured using various pressure units. Pressure is the force exerted per unit area, and vacuum is essentially a low-pressure environment.
There are different ways to measure vacuum, and understanding the concepts of relative and absolute vacuum is crucial in this context.
Pressure Units:
Torr: Named after Evangelista Torricelli, the Torr is a unit of pressure commonly used in vacuum measurements. It is equivalent to 1 millimetre of mercury (mmHg) pressure.
Pascal (Pa):
The SI unit of pressure. One pascal is defined as one newton per square meter.
Bar: A unit of pressure equal to 100,000 pascals.
Millibar (mbar):
Equal to one-thousandth of a bar.
Relative Vacuum:
Relative vacuum is measured with respect to atmospheric pressure. It expresses the pressure difference between the vacuum and the surrounding atmospheric pressure.
Common units for relative vacuum include inches of mercury (inHg) or millimetres of mercury (mmHg), as well as percentage of atmospheric pressure.
Absolute Vacuum:
Absolute vacuum is measured with respect to zero pressure or a perfect vacuum, theoretically the complete absence of matter.
The unit Torr is often used to measure absolute vacuum, where 0 Torr represents a perfect vacuum. Atmospheric pressure at sea level is around 760 Torr, so a vacuum of 100 Torr is 660 Torr below atmospheric pressure.
Vacuum Ranges:
Different applications require different levels of vacuum, and vacuum measurements can span a wide range. For example:
Low Vacuum: 760 Torr to 1 Torr (atmospheric pressure down to high vacuum).
Medium Vacuum: 1 Torr to 1 micro Torr.
High Vacuum: 1 micro Torr to 1 nano Torr.
Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV): Below 1 nano Torr.
What is the difference between relative and absolute vacuum?
Understanding the distinction between relative and absolute vacuum is crucial.
- Relative Vacuum:Relative vacuum refers to a pressure lower than the ambient pressure, but not necessarily a total absence of gases.It is often expressed in terms of the pressure difference between the vacuum and the surrounding atmosphere.In practical terms, it is a measure of how much lower the pressure is compared to the atmospheric pressure at a specific location.
- Absolute Vacuum:Absolute vacuum, on the other hand, refers to a complete absence of matter, including gases. It represents zero pressure.Achieving an absolute vacuum is theoretically impossible because there will always be some residual gas or particles present.Absolute vacuum is often used as a reference point, and pressures are measured relative to it. Standard atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 101325 pascals, and pressures lower than this are expressed as negative values.
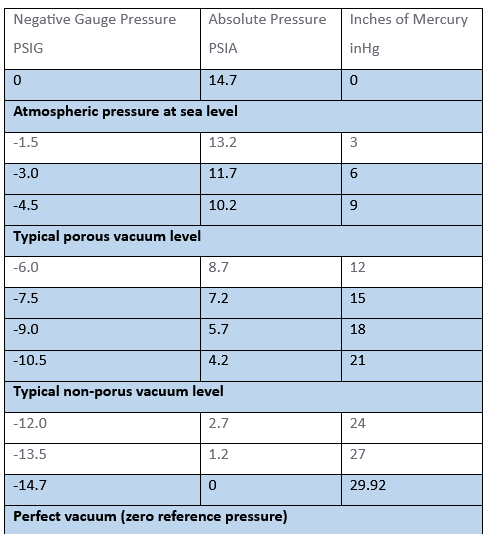
| Negative Gauge Pressure PSIG | Absolute Pressure PSIA | Inches of Mercury inHg |
| 0 | 14.7 | 0 |
| Atmospheric pressure at sea level | ||
| -1.5 | 13.2 | 3 |
| -3.0 | 11.7 | 6 |
| -4.5 | 10.2 | 9 |
| Typical porous vacuum level | ||
| -6.0 | 8.7 | 12 |
| -7.5 | 7.2 | 15 |
| -9.0 | 5.7 | 18 |
| -10.5 | 4.2 | 21 |
| Typical non-porous vacuum level | ||
| -12.0 | 2.7 | 24 |
| -13.5 | 1.2 | 27 |
| -14.7 | 0 | 29.92 |
| Perfect vacuum (zero reference pressure) | ||
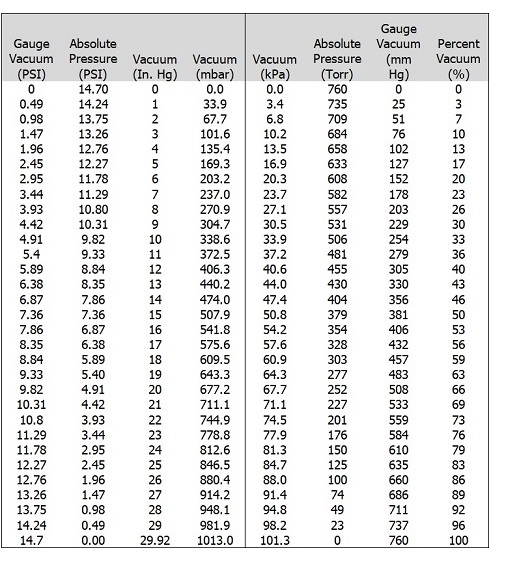
Vacuum Tables:
Gauge PSI, Absolute pressure PSI, Vacuum Inches Mercury, Vacuum millibar, vacuum kPa, Absolute pressure Torr, Gauge Vacuum mm mercury and percentage vacuum cross-reference guide.
Altitude feet, Altitude meters, absolute pressure and gauge pressure inches mercury vacuum conversion table.
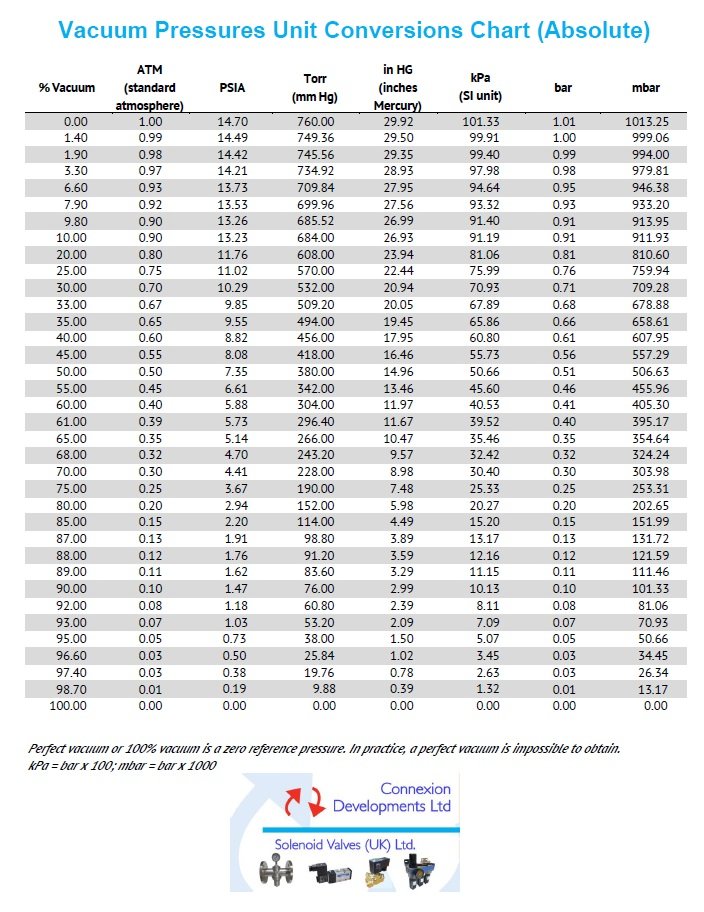
Vacuum pressure unit conversion chart (absolute)
Convert percentage vacuum, atmospheres, PSIA, Torr (millimetres mercury mm Hg), inches mercury In Hg, kPa (SI Unit), bar and mbar.
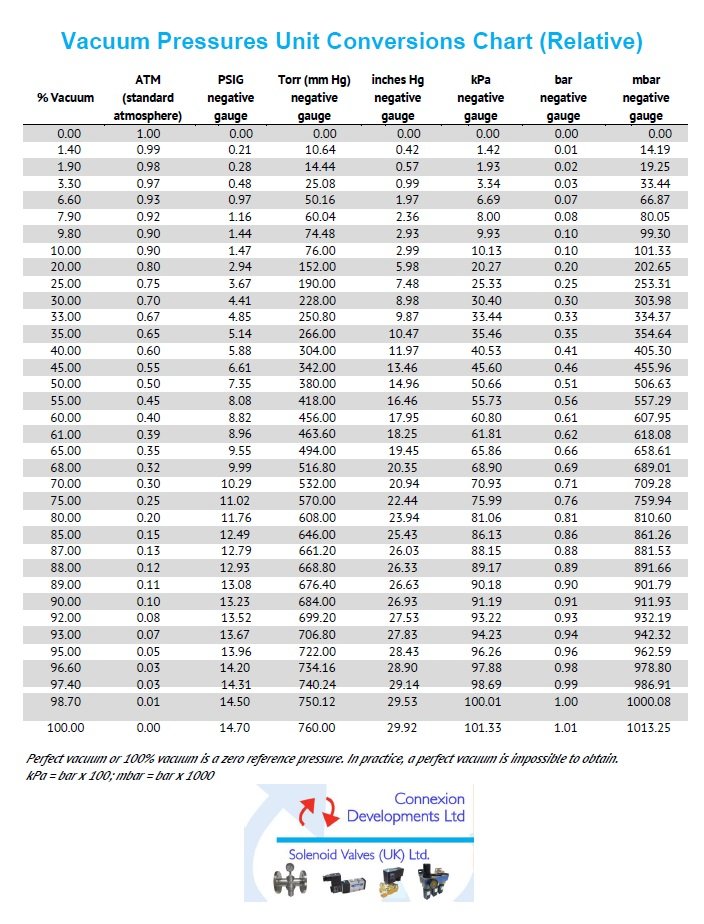
Vacuum pressure unit conversions chart (relative)
Percentage vacuum, atmosphere ATM, PSIG negative gauge pressure, Inches Mercury negative gauge, kPa negative gauge, bar negative gauge and millibar mbar negative gauge conversions.
Pascal (Pa)
Pa=N/m² : The Pascal (Pa) is the SI unit, 1 Bar = 10E5.Pa = 101 kPa = 0.1 MPa
A pressure of 1 Pa applied on a surface A=1m² generates a force F=1N (1N=1 kg.m.s-²).
1 Torr = 4/3 mbar, =133.3 Pa
1 standard atmosphere, 1 atm. = 760 Torr = 1013 mbar
1 tech. Atmosphere, 1 At = 1kp/cm² = 981 mbar
That relative Vacuum in %: V% = (Po-P)/Po, 300mbar => (1013-300)/1013= 70% Vacuum
or P=Po-(Po.V%), 30% in Torr => 760-(760.0.3)=532 Torr
atmospheric pressure (1 Atm.)
1.013 bar = 1013 millibars (mbar)
= 101325 Pascal (Pa), = 101 kPa
= 760 Millimetre mercury column (mmHgA) = 760 Torr (1 Torr = 1 mm HgA)
= 29.92 inches of mercury absolute (in HgA),
= 14.7 pounds per square inch absolute (lb/in², PSIA)
Atmospheric pressure is often measured with a mercury barometer, and a height of approximately 760 millimetres (30 in) of mercury is often used to illustrate (and measure) atmospheric pressure. However, since mercury is not a substance that humans commonly come in contact with, water often provides a more intuitive way to visualize the pressure of one atmosphere:
One atmosphere (101 kPa or 14.7 psi) is the amount of pressure that can lift water approximately 10.3 m (34 ft).
10.3 m (34 ft) is also the maximum height to which a column of water can be drawn up by suction / via a vacuum.
